| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In photolithography, a pattern may be transferred onto a photoresist film by exposing the photoresist to light through a mask of the pattern. In the semiconductor industry, the photolithographic procedure includes the following steps as illustrated in [link] : coating a base material with photoresist, exposing the resist through a mask to light, developing the resist, etching the exposed areas of the base, and stripping the remaining resist off.
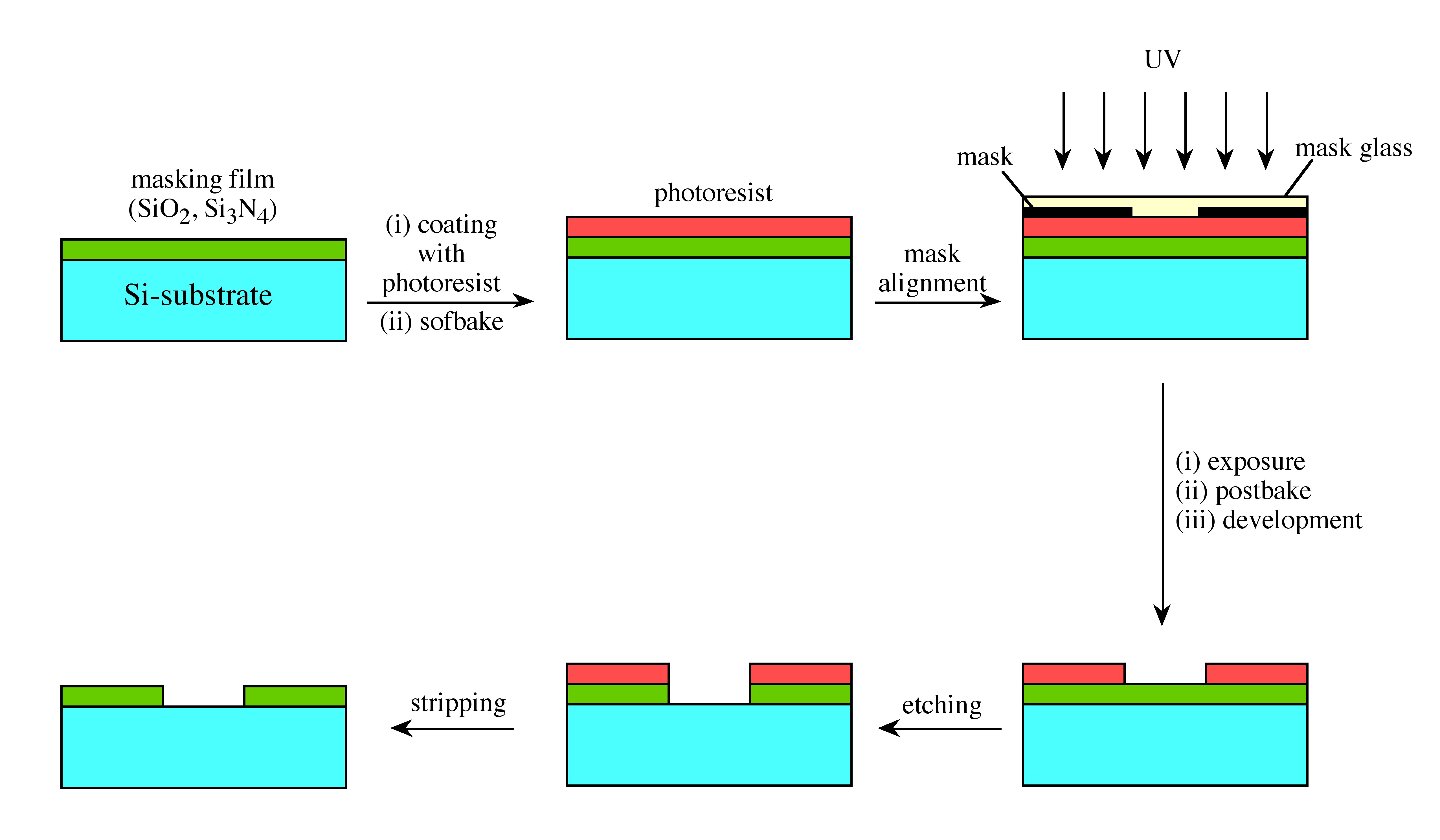
Upon exposure to light, the photoresist may become more or less soluble depending on the chemical properties of the particular resist material. The photochemical reactions include chain scission, cross-linking, and the rearrangement of molecules. If the exposed areas of the photoresist become more soluble, then it is a positive resist; conversely, if the exposed resist becomes less soluble, then it is a negative resist. In developing the photoresist, the more soluble material is removed leaving a positive or a negative image of the mask pattern.
Photoresists were initially developed for the printing industry. In the 1920s, the application of photoresists spread to the printed circuit board industry. Photoresists for semiconductor use were first developed in the 1950s; Kodak developed commercial negative photoresists and shortly after, Shipley developed a line of positive resists. Several other companies have entered the market since that time in hopes of manufacturing resist products which meet the increasing demands of the semiconductor industry: narrower line widths, fewer defects, and higher production rates.
Several functional requirements must be met for a photoresist to be used in the semiconductor industry. Photoresist polymers must be soluble for easy deposition onto a substrate by spin-coating. Good photoresist-substrate adhesion properties are required to minimize undercutting, to maintain edge acuity, and to control the feature sizes. The photoresist must be chemically resistant to whichever etchants are to be used. Sensitivity of the photoresist to a particular light source is essential to the functionality of a photoresist. The speed at which chemical changes occur in a photoresist is its contrast. The contrast of a resist is dependent on the molecular weight distribution of the polymers: a broad molecular weight distribution results in a low contrast resist. High contrast resists produce higher resolution images.
The four basic components of a photoresist are the polymer, the solvent, sensitizers, and other additives. The role of the polymer is to either polymerize or photosolubilize when exposed to light. Solvents allow the photoresist to be applied by spin-coating. The sensitizers control the photochemical reactions and additives may be used to facilitate processing or to enhance material properties. Photochemical changes to polymers are essential to the functionality of a photoresist. Polymers are composed primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen-based molecules arranged in a repeated pattern. Negative photoresists are based on polyisopreme polymers; negative resist polymers are not chemically bonded to each other, but upon exposure to light, the polymers crosslink, or polymerize. Positive photoresists are formulated from phenol-formaldehyde novolak resins; the positive resist polymers are relatively insoluble, but upon exposure to light, the polymers undergo photosolubilization.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of electronic materials' conversation and receive update notifications?