| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To emphasize the fact that every periodic signal has both a time and frequency domain representation, we can exploit both to encode information into a signal. Refer to the Fundamental Model of Communication . We have an information source, and want to construct a transmitter thatproduces a signal . For the source, let's assume we have information to encode every seconds. For example, we want to represent typed letters produced by anextremely good typist (a key is struck every seconds). Let's consider the complex Fourier series formula in the light of trying to encodeinformation.
Assume we have letters to encode: . One simple encoding rule could be to make a single Fouriercoefficient be non-zero and all others zero for each letter. For example, if occurs, we make and , . In this way, the harmonic of the frequency is used to represent a letter. Note that the bandwidth —the range of frequencies required for the encoding—equals . Another possibility is to consider the binary representation of the letter's index. For example, if theletter occurs, converting to its base 2 representation, we have . We can use the pattern of zeros and ones to represent directlywhich Fourier coefficients we "turn on" (set equal to one) and which we "turn off."
Compare the bandwidth required for the direct encoding scheme (one nonzero Fourier coefficient for each letter) to the binary number scheme. Compare the bandwidths for a128-letter alphabet. Since both schemes represent information without loss -- we can determine the typedletter uniquely from the signal's spectrum -- both are viable. Which makes more efficient use of bandwidth andthus might be preferred?
signals directly encoded require a bandwidth of . Using a binary representation, we need . For , the binary-encoding scheme has a factor of smaller bandwidth. Clearly, binary encoding is superior.
Can you think of an information-encoding scheme that makes even more efficient use of the spectrum? In particular, canwe use only one Fourier coefficient to represent letters uniquely?
We can use different amplitude values at only one frequency to represent thevarious letters.
We can create an encoding scheme in the frequency domain to represent an alphabet of letters. But, as thisinformation-encoding scheme stands, we can represent one letter for all time. However, we note that the Fourier coefficientsdepend only on the signal's characteristics over a single period. We could change the signal's spectrumevery as each letter is typed. In this way, we turn spectral coefficients on and off asletters are typed, thereby encoding the entire typed document. For the receiver (see the Fundamental Model of Communication ) to retrieve the typed letter, it would simply use the Fourier formula for the complex Fourier spectrum for each -second interval to determine what each typed letter was. [link] shows such a signal in the time-domain.
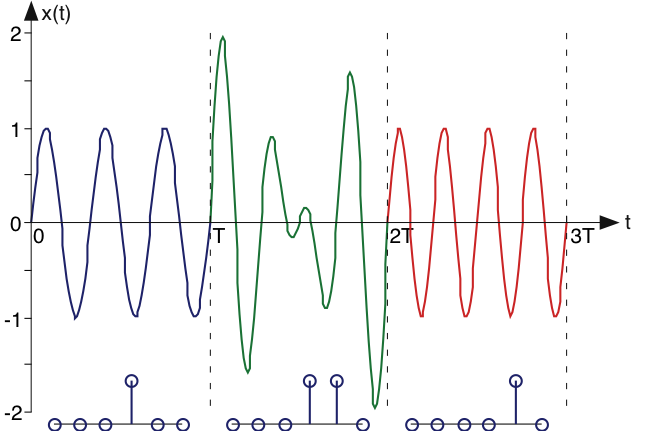
In this Fourier-series encoding scheme, we have used the fact that spectral coefficients can be independently specified andthat they can be uniquely recovered from the time-domain signal over one "period." Do note that the signal representing theentire document is no longer periodic. By understanding the Fourier series' properties (in particular that coefficients aredetermined only over a -second interval, we can construct a communications system. Thisapproach represents a simplification of how modern modems represent text that they transmit over telephone lines.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?