| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Activity 1:
To investigate and compare three-dimensional objects from the environment according to geometrical properties by making three-dimensional models using cut-out polygons
[LO 2.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5, 4.8]
1. Investigating nets: boxes.
You need a cornflake box, a box that contained tea and other boxes. Carefully open the boxes where they were glued so that they can be laid flat on the table. Examine the plan or net of the box.
2. Before you cut out the net below, fill in the dots for a dice on each face. Then cut out the net, fold it into a cube and stick it with sticky tape. Look at a real dice to see if your numbers are correct.
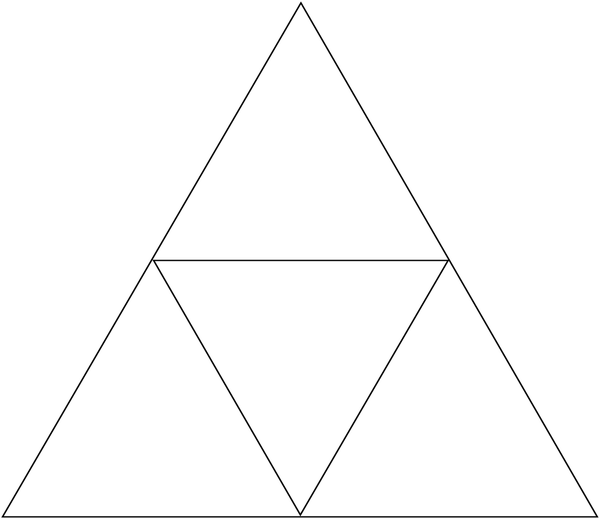
3. Cut out the shape below the table and fold it into a tetrahedron (a pyramid) with three sides and a triangular base.
4. Now use the net of the cornflake box (rectangular prism), the cube that you have cut out and the tetrahedron to complete the table:
| Object | Number of surfaces | Flat or curved surfaces (faces) | Number of corners (vertices) | Number of edges |
| Rectangular prism | ||||
| Cube | ||||
| Tetrahedron |
Activity 2:
To recognise and describe lines of symmetry in two-dimensional shapes including those in nature and its cultural art forms
[LO 3.4]
1. PROJECT.
2. Shapes.
2.1 Cut out the shapes below. See if each of them can be folded in half. The fold is called a LINE OF SYMMETRY. Use a ruler to make a dotted line on the fold. Some shapes have more than one line of symmetry. Remember that both halves must be identical. Draw in all the lines of symmetry and paste the shapes on top of the shapes on this page. Label your lines of symmetry.
2.2 Make other shapes, e.g. a circle, and fold them to find lines of symmetry. Paste them on the clean sheet as well. Label the lines of symmetry.


Activity 3:
To describe changes in the view of an object held in different positions
[LO 3.7]
If we see a large building from the front, we know that it will not look the same if we see it from the back or from the side or if we are standing in front of a corner of the building.
1.
1.1 Go outside and look at the school from the front.
1.2 Walk round to the back of the school and look at it again.
When seen from each of the above positions, the school looks amazingly different.
2. Make the objects below with sugar cubes and look at them from various angles.
3. Make some more objects with sugar cubes and examine them from the front, the back, the sides and the corners.
4. Draw the following objects as they would look if you saw them from:
4.1 behind:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?