| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The operation of downsampling by factor describes the process of keeping every sample and discarding the rest. This is denoted by " " in block diagrams, as in [link] .
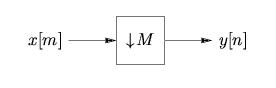
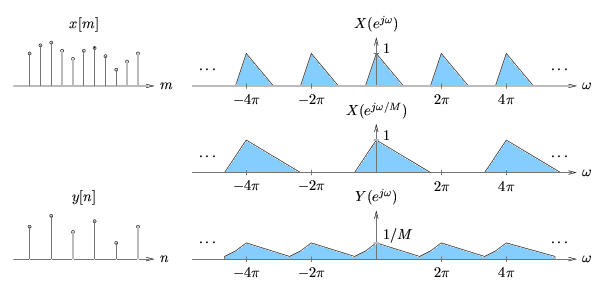
Formally, downsampling can be written as In the domain,
As shown in [link] , downsampling expands each -periodic repetition of by a factor of along the axis, and reduces the gain by a factor of . If is not bandlimited to , aliasing may result from spectral overlap.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of signal processing' conversation and receive update notifications?