| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When we find the differential equation relating the source and the output, we are faced with solving the circuit in what isknown as the time domain . What we emphasize here is that it is often easier to find the output if we useimpedances. Because impedances depend only on frequency, we find ourselves in the frequency domain . A common error in using impedances is keeping the time-dependent part,the complex exponential, in the fray. The entire point of using impedances is to get rid of time and concentrate onfrequency. Only after we find the result in the frequency domain do we go back to the time domain and put things back togetheragain.
To illustrate how the time domain, the frequency domain and impedances fit together, consider the time domain and frequencydomain to be two work rooms. Since you can't be two places at the same time, you are faced with solving your circuit problemin one of the two rooms at any point in time. Impedances and complex exponentials are the way you get between the two rooms.Security guards make sure you don't try to sneak time domain variables into the frequency domain room and vice versa. [link] shows how this works.
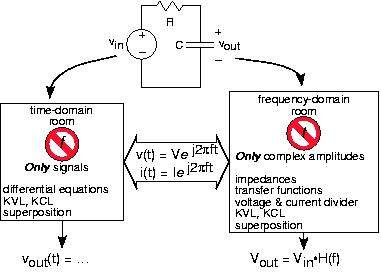
As we unfold the impedance story, we'll see that the powerful use of impedances suggested by Steinmetz greatly simplifies solving circuits, alleviates us from solving differential equations, and suggests a general way of thinkingabout circuits. Because of the importance of this approach, let's go over how it works.
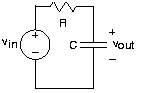
To illustrate the impedance approach, we refer to the circuit ( [link] ) below, and we assume that .
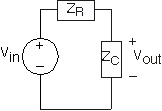
Using impedances, the complex amplitude of the output voltage can be found using voltage divider:
If we refer to the differential equation for this circuit (shown in Circuits with Capacitors and Inductors to be ), letting the output and input voltages be complex exponentials, we obtain the same relationship between theircomplex amplitudes. Thus, using impedances is equivalent to using the differential equation and solving it when the sourceis a complex exponential.
In fact, we can find the differential equation directly using impedances. If we cross-multiply the relation between input and output amplitudes, and then put the complex exponentials back in, we have In the process of defining impedances, note that the factor arises from the derivative of a complex exponential. We can reverse the impedance process, and revertback to the differential equation. This is the same equation that was derived much more tediously in Circuits with Capacitors and Inductors . Finding the differential equation relating output to input is far simpler when we use impedancesthan with any other technique.
Suppose you had an expression where a complex amplitude was divided by . What time-domain operation corresponds to this division?
Division by arises from integrating a complex exponential. Consequently,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?