| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
For the educator:
This module, “Willy goes fishing”, gives learners the opportunity to discuss different kinds of sport. Learners discuss sporting activities in which they take part and collect photos, news items and posters that they bring to school.
The educator can tape a variety of comments of matches. Learners listen and identify which sport is being played. Learners therefore listen without seeing the speaker, to develop auditory perception. Tapes of stories should be a regular activity to listen to in the Foundation Phase classroom. (LO/AS 1.7,)
To correlate with the theme, the educator can design a “fishing game” to test the vocabulary learnt in previous modules. The words can be written on cards, a paper-clip attached to each card, a fishing rod made with an open paper-clip on the end and learners can take turns to “catch a fish” and read the word on the card.
In the previous module the “nd” and “mp” sounds at the end of words were introduced. In this module these words are revised and the “ck” sound is introduced.
Write these words on flash cards and teach them as sight words to the learners: sport; cricket; tennis; hockey; rugby; soccer; netball and fishing.
The topic of this module revolves around sport. Learners realize all children should be able to take part in sport – Human rights. There should be amenities for everybody. Sports facilities provide a safe playing area for everybody, provide healthy recreational
Writing stories.
The six pictures can be enlarged.
Divide the class into groups and give each group a blank piece of paper and one of the pictures. Every group must write four sentences about their picture. The educator will assist the groups with the writing of words. Each learner in the group can be responsible for a different task, e.g. one can cut out the picture, one can find a word in the flip file, etc. Everyone in the group must be able to read their four sentences. At the end of the lesson all the stories can be joined together to make one long story.
Newspaper activities.
Let the learners bring newspapers to school.
Divide the class into four or five groups.
Do the activity planned on the next page (p. 22).
Also use newspapers for the following activities:
1. Cut out letters to build the names of the learners in a group.
2. Find a picture that depicts a happy person and one of an unhappy person.
3. Find four words that your group can read. Cut them out and paste them on a piece of paper.
4. Cut out three words and make sentences with them.
5. Find words beginning with a “b”.
6. Find words that end in “nd” and “mp”.
Read them and draw the pictures.
| LO 2.8 | LO 4.5.1 | LO6.2 |
| LO 2.7 | LO 4.4.1 | LO 4.4.2 | LO 4.4.3 | LO 6.3.3 |

| LO 4.1.2 | LO 4.1.3 |

| LO 3.1.2 | LO 3.2.3 |

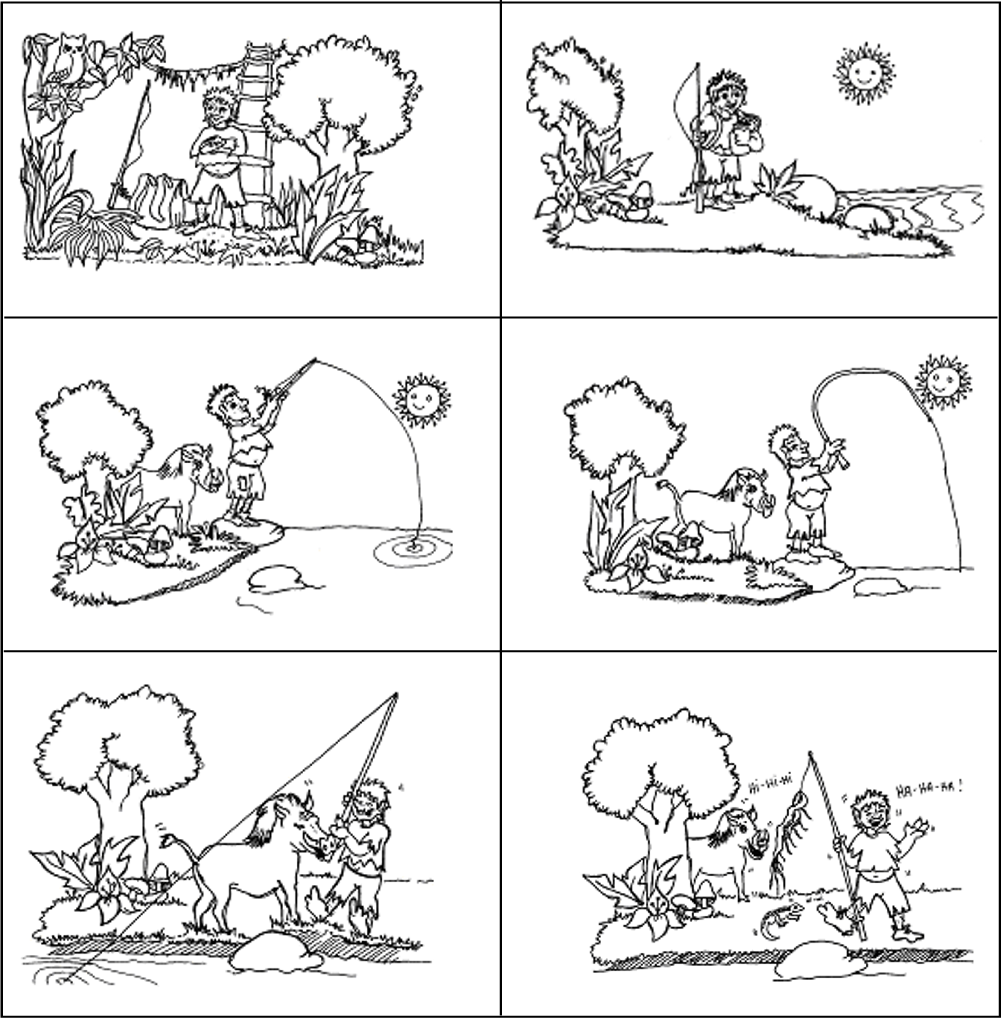
Willy wants to play cricket.
He has a bat and a ball.
Dad made the bat.
Licky, Walter, Sam and Terry
also want to play.
Willy hits the ball.
The ball falls in the river.
Sam finds it.
Now it is Walter’s turn.
| LO 3.1.2 | LO 3.2.3 |
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner uses visual clues to make meaning:
3.1.2 uses illustrations to interpret the meaning of stories, and tells a story;
Assessment Standard 3.2: We know this when the learner role-plays reading:
3.2.3 looks at words and pictures;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.1: We know this when the learner writes with increasing legibility:
4.1.2 writes with increasing legibility:
4.1.3 forms letters of the alphabet successfully;
Assessment Standard 4.4: We know this when the learner drafts and revises:
4.4.1 contributes ideas to a group writing a story;
4.4.2 revises a draft of the group’s story to be clearer and more interesting;
4.4.3 writes and reads own draft to teacher and classmates, and starts to make revisions;
Assessment Standard 6.3: We know this when the learner works with sentences:
6.3.3 uses nouns, pronouns and prepositions correctly.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English home language grade 1' conversation and receive update notifications?