| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
SSPD_Chapter 1_Part10_concluded_ ENERGY BAND THEORY IN A SOLID BASED ON KRONIG-PENNEY MODEL.
Kronig-Penney model is 1-D array of square wells as shown in Figure 1.44.. This is 1-D idealization of a linear array of atoms in a single crystal lattice structure. The solution of Schrodinger Equation using this array of Square wells becomes more tractable and it still brings out the important features of the quantum behavior of electrons in real life crystalline periodic lattice.
There are four assumptions in Kronig-Penney Model analysis namely:
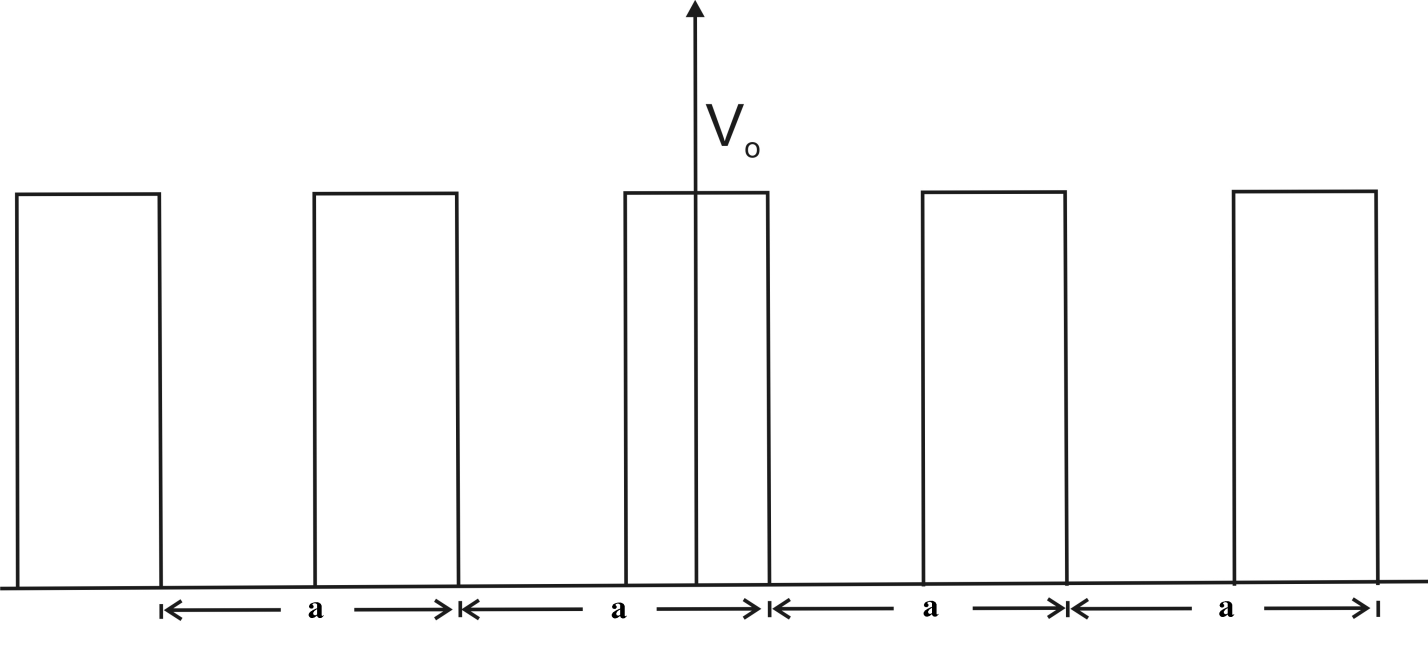
Figure 1.44. Kronig-Penny Model of a linear array of atoms in a single crystal solid.
The solution of Schrodinger Equation can be arrived at mathematically but for simplicity of presentation we will discuss the problem in qualitative terms only.
Study of electron in a crystalline structure is really the study of an electron in a periodically varying potential field. For simplicity of analysis we assume a linear array of
atoms . The crystal length is L cm. Let Z-axis be the longitudinal axis and let the crystal be repeated along the Z-axis with a period of L cm from - ∞ to + ∞ . Along X-axis and Y-axis it is of infinite length. So we have a semi-infinite crystal of finite length L cm in Z-axis. For the ease of calculation we assume that crystal is repeated along z-axis at L cm.
Since we have assumed a periodic crystalline structure along Z axis therefore the solution of the Schrodinger Equation is applicable only in the bulk and not at the boundaries of the crystal.
We will assume that L cm = 1cm =1×10 -2 m. The crystal structure is referred to as the lattice. The atoms of the crystal are referred to as the lattice centers. The distance between two consecutive lattice centers is referred to as the lattice constant ‘a’ Å. A typical lattice constant is 2 Å. Therefore the linear array contains L/a = 1×10 -2 m/2×10 -10 m = 5×10 7 atoms in one period. Let this number be N i.e. N= 5×10 7 .
We have a periodically varying potential field along the linear array with a periodicity of ‘a’ Å hence the Fourier Series Expansion of the potential is:
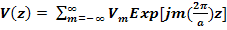
The potential field has a period of ‘a’ Å hence 2π/a is the fundamental periodicity and the harmonics are 2(2π/a) , 3(2π/a) , 4(2π/a) …………………..m(2π/a)
In the periodic potential field following is the Schrodinger Equation for time independent part:
∂ 2 ψ/∂z 2 + [{2m(E-V(z))}/ћ 2 ]ψ = 0............ 1.84
If we had assumed that our very wide potential well was flat bottomed with V(z) = 0 everywhere along the potential box then the solution of the Schrodinger Equation would be a progressive wave as would be obtained for free space:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Solid state physics and devices-the harbinger of third wave of civilization' conversation and receive update notifications?