| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
SSPD_Chapter 1_Part 10_continued_EXPLANATION OF ENERGY BAND THEORY BASED ON HEISENBERG’S UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states:
∆x.∆p x ≥ ћ/2
∆t.∆E ≥ ћ/2 1.82
In a single Hydrogen Atom, when an electron jumps from the ground state to excited state then electron stays in the excited state for 10 nanoseconds. On atomic time scale this life-time in excited state is considered to be long. By Hiesenberg’s Uncertainty Principle a large temporal uncertainty in excited state makes the energy level less uncertain. The excited states have uncertainty of only 10 -7 eV. This means the energy spread has a magnitude of 10 -7 eV. Hence in single atoms all the states are discrete.
In a crystalline lattice on the contrary, the electrons stay at the excited state only for femtoseconds (10 -15 seconds). Because of this very reduced temporal uncertainty in the lifetime of excited state a very large uncertainty, almost of the order of 1eV, creeps in the excited energy state. This leads to spreading of discrete energy states in a single atom to energy bands of the order of 1eV in a single crystal solid.
Why is the uncertainty in the life-time at higher energy states in a solid so minimal?
In a single atom, an electron is trapped in an infinite potential well hence we have well defined discrete energy states as permissible energy states. On the contrary in a crystalline solid, valence electrons are trapped in an array of finite potential wells and the potential walls dividing the potential wells are of finite thickness. This results in a finite quantum-mechanical tunneling probability of excited state electrons . This tunneling probability is higher for higher excited states. Because of this quantum mechanical tunneling phenomena, electrons are highly unstable at the excited states and they immediately return to the ground state. This explains the negligible uncertainty or negligible spread in the lifetime of excited electrons. Smaller is the spread in the lifetime larger is the energy spread of the excited state. As we go to outer orbits, meaning by as we go to higher energy states we have broader energy bands as seen in Fig (1.41.b&c). The innermost energy bands are the narrowest and the outermost are the broadest.
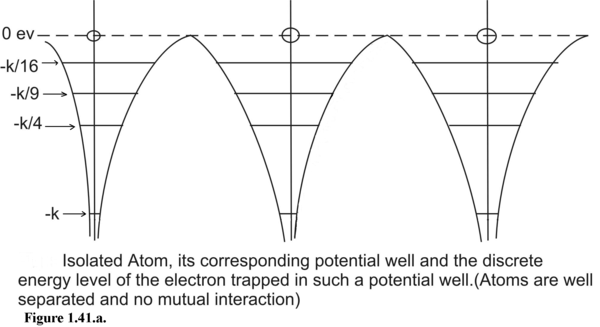
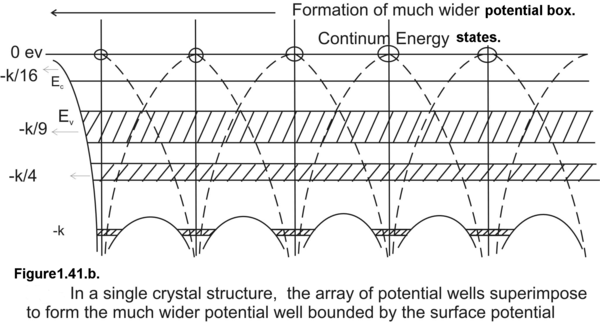
Figure 1.41. Comparative study of the potential well of an isolated atom and the much wider potential box created by a crystalline solid.
If there is 1-D array of atoms well separated as shown in Figure 1.41.a, the electrons continue to occupy discrete energy states given by the formula :
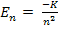
But as the inter-atomic distances are reduced and electrons in individual potential wells start interacting the discrete energy states start spreading out in closely spaced energy levels. This cluster of closely spaced energy states appear as a permissible band of energy states.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Solid state physics and devices-the harbinger of third wave of civilization' conversation and receive update notifications?