| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In some (complicated) cases, we cannot use the simplification techniques--such as parallel or series combination rules--tosolve for a circuit's input-output relation. In other modules, we wrote v-i relations and Kirchoff's laws haphazardly, solving them more on intuition than procedure. Weneed a formal method that produces a small, easy set of equations that lead directly to the input-output relation weseek. One such technique is the node method .
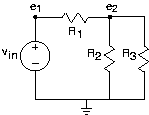
The node method begins by finding all nodes--places where circuit elements attach to each other--in the circuit. We callone of the nodes the reference node ; the choice of reference node is arbitrary, but it is usually chosen to be apoint of symmetry or the "bottom" node. For the remaining nodes, we define node voltages that represent the voltage between the node and the reference.These node voltages constitute the only unknowns; all we need is a sufficient number of equations to solve for them. In ourexample, we have two node voltages. The very act of defining node voltages is equivalent to using all the KVLequations at your disposal . The reason for this simple, but astounding, fact is that a node voltage is uniquelydefined regardless of what path is traced between the node and the reference. Because two paths between a node and referencehave the same voltage, the sum of voltages around the loop equals zero.
In some cases, a node voltage corresponds exactly to the voltageacross a voltage source. In such cases, the node voltage is specified by the source and is not an unknown. For example, in our circuit, ; thus, we need only to find one node voltage.
The equations governing the node voltages are obtained by writingKCL equations at each node having an unknown node voltage, using the v-i relations for each element. In our example, the only circuit equation is
Have we really solved the circuit with the node method? Alongthe way, we have used KVL, KCL, and the v-i relations. Previously, we indicated that the set of equations resulting from applying these laws is necessary and sufficient.This result guarantees that the node method can be used to "solve" any circuit. One fallout of this result is that we must be able to find any circuit variablegiven the node voltages and sources. All circuit variables can be found using the v-i relations and voltage divider. For example, the current through equals .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?