| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
SSPD_Chapter 1_Part 8_ ELECTRON IN 1-D POTENTIAL WELL_Formulation of Schrodinger Equation.
One Dimensional Potential Well can be of three types:
Before analyzing electron in a potential well we will give the physical significance of matter wave.
Like electromagnetic waves, matter wave is a progressive or traveling harmonic wave.
For mathematical simplicity we will deal with waves having plane wavefront. These are called Plane Waves.
There can be traveling waves of spherical wavefront or cylindrical wavefront and these are known as spherical waves or cylindrical waves respectively.
In fact a spherical wave or cylindrical wave becomes a plane wave after they have traveled for a very long distance. As long as radius of curvature is finite we have cylindrical or spherical curvature and curvature is defined as 1/r where r is the radius of curvature. As soon as radius of curvature is infinite as it would be if the wave has traveled for a very long distance , the curvature becomes zero and the wave assumes a plane wavefront and it is called Plane Wave.
In Fig.(1.21) a Plane Transverse Electro-Magnetic Wave is shown.
E(z,t) = E x0 Exp[j(k z .z – ω.t)]
H(z,t) = H y0 Exp [j(k z .z - ω.t)] 1.41
Where k z = 2π/λ z = wave propogation vector or wave number;
And ω = 2 π ν = circular frequency;
A wave front is defined as front on which all points have same phase. If this front is plane we say we have a plane wave. If the front is cylindrical, we have cylindrical waves and if the wave front is spherical we have spherical waves.
The wave front moves with a velocity . This wave front velocity is the velocity of wave propogation.
i.e. k z .z - ω.t = constant = K
Taking the time derivative we obtain:
k z .∂z/∂t - ω.= 0
rearranging the terms we get: .
∂z/∂t = ω/ k z = λ z . ν = velocity of the progressive wave front.
A phase term of the form (k z .z - ω.t) gives a forward traveling wave
whereas a phase term of the form(k z .z + ω.t) gives a backward traveling wave.
In absolute vacuum Electromagnetic Wave travels with velocity of light c=3×10 8 m/sec.
In absolute vacuum, ω/k z = λ z .ν = c = 3×10 8 m/sec (velocity of light, in absolute vacuum,is suppose to be an invariant quantity i.e. invariant with respect to the frame of reference [Lorentz Invariance or Gauge Invariance – Appendix XXIX ] . This fact was established by Albert Abraham Michelson(1852-1931) and Edward Williams Morley(1838-1923) in their celebrated experiment known as Michelson-Morley experiment [Appendix XXXIII ] . This is called Special Theory of Relativity which was propounded by Einstein in 1905).The Eq.(1.41) is the solution of the wave equation given in Appendix(XXXIV) .
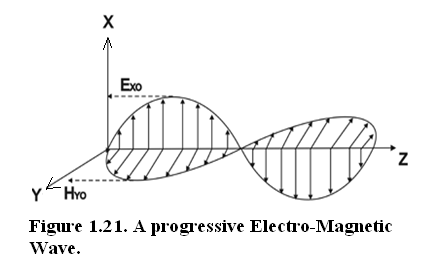
Fig(1.21) A Progressive Plane Electro-Magnetic Wave.
An electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave because the oscillation is transverse to the direction of propagation. Electric field is oscillating in X direction and Magnetic Field is oscillating in Y direction whereas Z axis is the direction of propagation. Here X and Y axes are transverse to Z-axis. Maxwell equations constrain Electric field and Magnetic Field to be perpendicular to each other and also to the direction of propagation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Solid state physics and devices-the harbinger of third wave of civilization' conversation and receive update notifications?