| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If the source consists of two (or more) signals, we know from linear system theory that the output voltage equalsthe sum of the outputs produced by each signal alone. In short, linear circuits are a special case of linear systems, andtherefore superposition applies. In particular, suppose these component signals are complex exponentials, each of which has afrequency different from the others. The transfer function portrays how the circuit affects the amplitude and phase of eachcomponent, allowing us to understand how the circuit works on a complicated signal. Those components having a frequency lessthan the cutoff frequency pass through the circuit with little modification while those having higher frequencies aresuppressed. The circuit is said to act as a filter , filtering the source signal based on the frequency of eachcomponent complex exponential. Because low frequencies pass through the filter, we call it a lowpass filter to express more precisely its function.
We have also found the ease of calculating the output forsinusoidal inputs through the use of the transfer function. Once we find the transfer function, we can write the output directlyas indicated by the output of a circuit for a sinusoidal input .
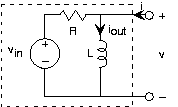
Let's apply these results to a final example, in which the input is a voltage source and the output is the inductorcurrent. The source voltage equals . We want the circuit to pass constant (offset) voltageessentially unaltered (save for the fact that the output is a current rather than a voltage) and remove the 60 Hz term.Because the input is the sum of two sinusoids--a constant is a zero-frequency cosine--our approach is
The constant term is easiest to handle. The output is given by . Thus, the value we choose for the resistance will determinethe scaling factor of how voltage is converted into current. For the 60 Hz component signal, the output current is . The total output due to our source is
The phase of the 60 Hz component will very nearly be , leaving it to be . The waveforms for the input and output are shown in [link] .
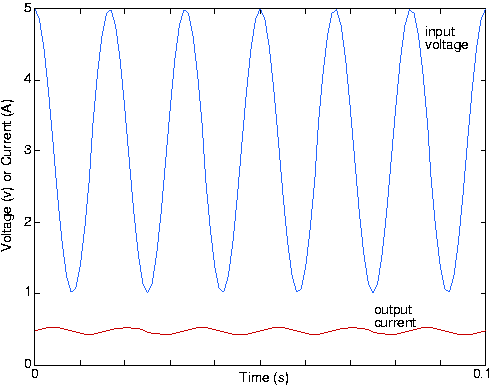
Note that the sinusoid's phase has indeed shifted; the lowpass filter not only reduced the 60 Hz signal's amplitude, but alsoshifted its phase by 90°.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?