| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The ratio of the output and input amplitudes for [link] , known as the transfer function or the frequency response , is given by
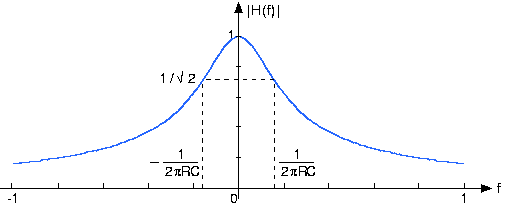
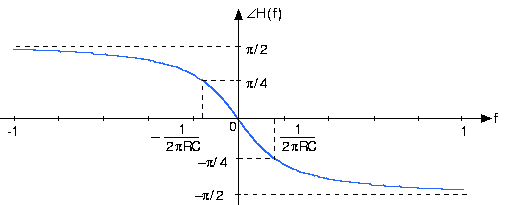
This transfer function has many important properties and provides all the insights needed to determine how the circuit functions. First of all, note that we can compute the frequency response for both positive andnegative frequencies. Recall that sinusoids consist of the sum of two complex exponentials, one having the negative frequencyof the other. We will consider how the circuit acts on a sinusoid soon. Do note that the magnitude has even symmetry : The negative frequency portion is a mirror image of the positive frequency portion: . The phase has odd symmetry : . These properties of this specific example apply for all transfer functions associated withcircuits. Consequently, we don't need to plot the negative frequency component; we know what it is from the positivefrequency part.
The magnitude equals of its maximum gain (1 at ) when (the two terms in the denominator of the magnitude are equal). The frequency defines the boundary between two operating ranges.
The phase shift caused by the circuit at the cutoff frequencyprecisely equals . Thus, below the cutoff frequency, phase is little affected, but athigher frequencies, the phase shift caused by the circuit becomes . This phase shift corresponds to the difference between a cosine and a sine.
We can use the transfer function to find the output when theinput voltage is a sinusoid for two reasons. First of all, a sinusoid is the sum of two complex exponentials, each having afrequency equal to the negative of the other. Secondly, because the circuit is linear, superposition applies. If the source isa sine wave, we know that
This input-output property is a special case of a more general result. Show that if the source can be written asthe imaginary part of a complex exponential— — the output is given by . Show that a similar result also holds for the real part.
The key notion is writing the imaginary part as the difference between a complex exponential and its complexconjugate:
The notion of impedance arises when we assume the sources arecomplex exponentials. This assumption may seem restrictive; what would we do if the source were a unit step? When we useimpedances to find the transfer function between the source and the output variable, we can derive from it the differentialequation that relates input and output. The differential equation applies no matter what the source may be. As we have argued, it isfar simpler to use impedances to find the differential equation (because we can use series and parallel combination rules) thanany other method. In this sense, we have not lost anything by temporarily pretending the source is a complex exponential.
In fact we can also solve the differential equation usingimpedances! Thus, despite the apparent restrictiveness of impedances, assuming complex exponential sources is actuallyquite general.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?