| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
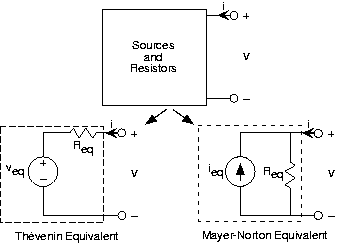
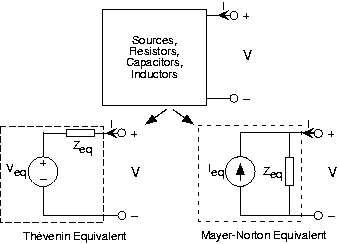
When we have circuits with capacitors and/or inductors as wellas resistors and sources, Thévenin and Mayer-Norton equivalent circuits can still be defined by using impedances andcomplex amplitudes for voltage and currents. For any circuit containing sources, resistors, capacitors, and inductors, theinput-output relation for the complex amplitudes of the terminal voltage and current is with . Thus, we have Thévenin and Mayer-Norton equivalentcircuits as shown in [link] .
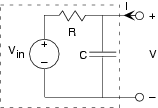
Let's find the Thévenin and Mayer-Norton equivalent circuitsfor [link] . The open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current techniques still work, except we useimpedances and complex amplitudes. The open-circuit voltage corresponds to the transfer function we have alreadyfound. When we short the terminals, the capacitor no longer has any effect on the circuit, and the short-circuit current equals . The equivalent impedance can be found by setting the source tozero, and finding the impedance using series and parallel combination rules. In our case, the resistor and capacitor arein parallel once the voltage source is removed (setting it to zero amounts to replacing it with a short-circuit). Thus, . Consequently, we have Again, we should check the units of our answer. Note in particular that must be dimensionless. Is it?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?