| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Fossils are the remains of dead plants, animals, bacteria and other life forms that lived millions of years ago and were then petrified.
Fossils are the petrified remains of organisms, e.g. teeth, bones, bark or shells. They may also be the tracks or waste products of organisms.
1. When an animal or organism dies, the soft parts decay first. The rest is buried below the sand or in mud.
2. Over millions of years, chemical changes and the intense pressure of overlying layers result in the petrification of these remains.
3. Water that seeps through such remains also effects changes. Petrified forms are retained very well.
4. Movement of the earth plates brings fossils to the surface.
What is a palaeontologist?
What does SA law say about fossils? www.ru.ac.za/pssa/pssalaw.html
Assessment of the flow diagram:
Were you able to draw a meaningful flow diagram of the fossilisation process?
[ LO 2.2]
Adaptations – Fossils
Study the following sketches of fossils and try to make deductions concerning their feeding and locomotion:
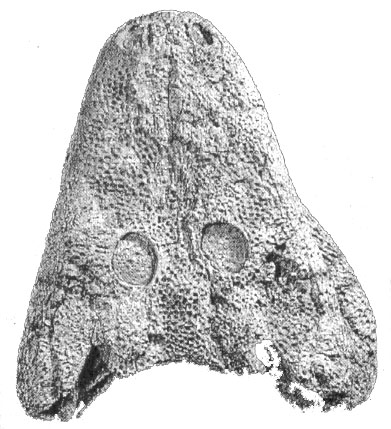
Skull of a primitive amphibian

Brachiopod shells in a 500 – 300 million year-old marine deposit

Skull of a South African dinosaur ( Mossospondylus )
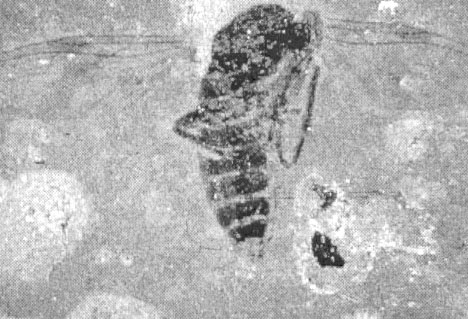
A fly found in the 90 million years old deposits of the Orapa diamond crater (Botswana)
Assessment of deduction:
Could you make correct deductions from the pictures of fossils?
[ LO 2.3]
Learning outcomes 2: Constructing Science Knowledge
The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
This is evident when the learner
Class activity: SKETCHES of FOSSILS

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 8' conversation and receive update notifications?