| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
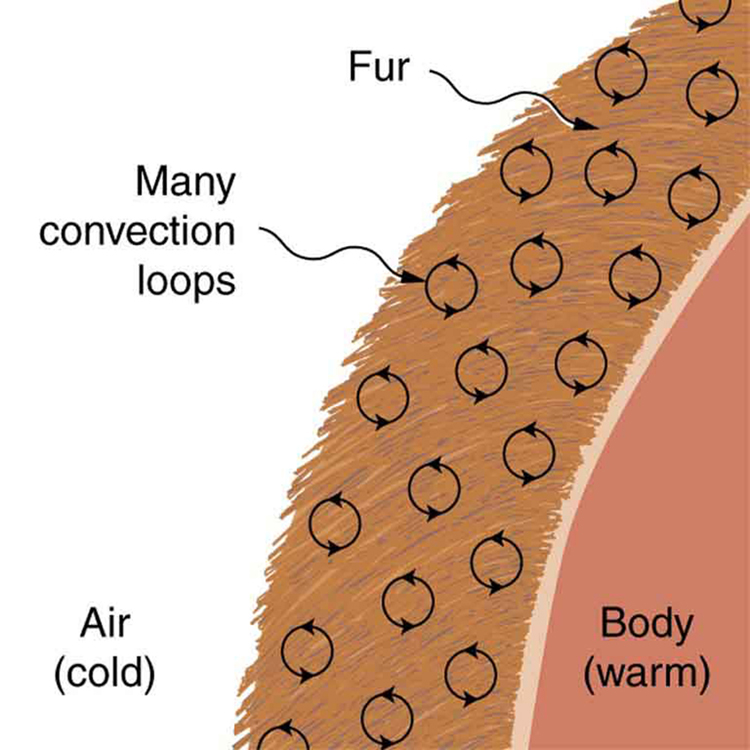
Some interesting phenomena happen when convection is accompanied by a phase change . It allows us to cool off by sweating, even if the temperature of the surrounding air exceeds body temperature. Heat from the skin is required for sweat to evaporate from the skin, but without air flow, the air becomes saturated and evaporation stops. Air flow caused by convection replaces the saturated air by dry air and evaporation continues.
The average person produces heat at the rate of about 120 W when at rest. At what rate must water evaporate from the body to get rid of all this energy? (This evaporation might occur when a person is sitting in the shade and surrounding temperatures are the same as skin temperature, eliminating heat transfer by other methods.)
Strategy
Energy is needed for a phase change ( ). Thus, the energy loss per unit time is
We divide both sides of the equation by to find that the mass evaporated per unit time is
Solution
(1) Insert the value of the latent heat from [link] , . This yields
Discussion
Evaporating about 3 g/min seems reasonable. This would be about 180 g (about 7 oz) per hour. If the air is very dry, the sweat may evaporate without even being noticed. A significant amount of evaporation also takes place in the lungs and breathing passages.
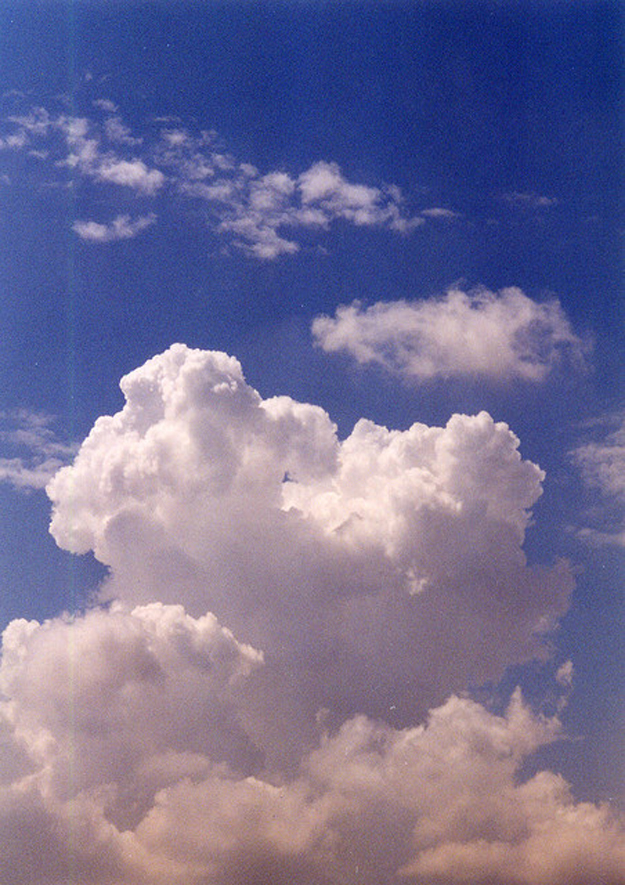
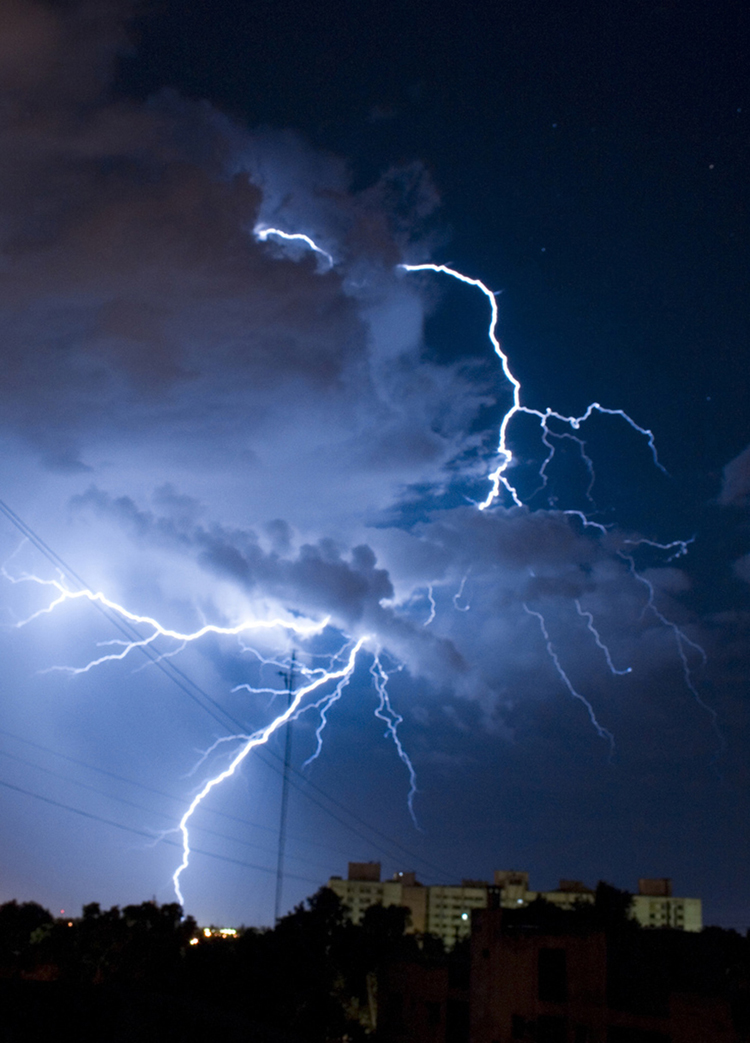
Another important example of the combination of phase change and convection occurs when water evaporates from the oceans. Heat is removed from the ocean when water evaporates. If the water vapor condenses in liquid droplets as clouds form, heat is released in the atmosphere. Thus, there is an overall transfer of heat from the ocean to the atmosphere. This process is the driving power behind thunderheads, those great cumulus clouds that rise as much as 20.0 km into the stratosphere. Water vapor carried in by convection condenses, releasing tremendous amounts of energy. This energy causes the air to expand and rise, where it is colder. More condensation occurs in these colder regions, which in turn drives the cloud even higher. Such a mechanism is called positive feedback, since the process reinforces and accelerates itself. These systems sometimes produce violent storms, with lightning and hail, and constitute the mechanism driving hurricanes.




Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics 105: adventures in physics' conversation and receive update notifications?