| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Grade 3 learners continue to expand their vocabulary by listening and reading a variety of texts such as poem, stories, riddles and doing word puzzles.
These modules consolidate and revise the vocabulary and phonics introduced in Grade 2. More opportunities are given for written work producing longer texts of more varied kinds. Learners should not be afraid to make mistakes as the building of confidence and fluency should take priority above perfect written work.
Time scheduled for the modules
All learners should work through all eight modules as the phonics and spelling requirements are spread over these modules. The educator should however allow learners to complete them at their own pace namely ± two modules per term.
The story of “The Sly Old Fox” gives learners the opportunity to discuss such moral issues as honesty, truthfulness and faithfulness.
Learners write the dialogue between the characters.
A graph is kept for recording results of future spelling tests.
They read a factual article on crabs and make up their own story stimulated by a picture.
Integration of themes
We have a responsibility towards our friends. We need to be loyal, honest and helpful.
1 across: The …………………………………………………………. goes fast.
1 down: B…………………………………………………………. you said yes.

1 across: The dog is full of m……………………………………………………..
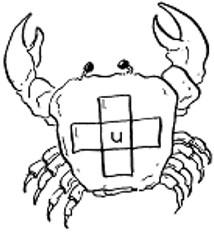
1 across: The ……………………………………………………………… is hot.
1 down: We will have f …………………………………………………………..
| LO 4.1 | LO 4.3 |
1 across: I eat a …………………………………………………………………...
1 down: My …………………………………………………………….. is right.

I across: I build a …………………………………………………………………
1 down: I wash my dog in a ……………………………………………………..

1. The s . . . . . . . is h . . . . . . .t.
2. Put the b . . . . . . n in the . . . . . . . . . .
3. Do n. . . . . . .t play in the m . . . . . . . d.
4. Will you r. . . . . . .b a f. . . . . . . .x.?
| LO 4.1 | LO 4.3 |

Use the words for writing your English stories.
| apples | animals | bridge | big | cross |
| comes | clothes | cat | chair | cow |
| cupboard | cap | dog | dwarf | eat |
| field | fruit | dress | furniture | goats |
| grass | horse | jacket | jersey | jeans |
| over | oranges | peaches | runs | shoes |
| shirt | trousers | the | friend | story |
| listen | read | fox | sly | clever |
| always | crabs | scurrying | swim | boat |
| other | camel | place | corn | ripe |
| barley | tail | heard | beat | middle |
| deep | roll | rolled | who | watermelon |
| LO 5.5 |

Some crabs live on land.
Some crabs live in the sea.
There are blue crabs and red crabs
and purple crabs and green crabs.
The crabs that live in the sand
are the colour of the sand.
Crabs have eyes on stalks.
They have many legs.
Some crabs are big.
Some crabs are small.
Some crabs feed on young leaves.
Crabs that live in the sea come
out onto the beach to eat any tiny
dead or alive creatures.
They catch them with their first pair of legs,
which can pinch. These are called pincers.
Be careful when walking bare feet on the beach.
A crab might think your toe will make a good dinner!
| LO 3.3.1 | LO 3.8.4 | LO 6.6 |

| LO 2.5 | LO 2.10 | LO 4.10 | LO 5.7.3 |
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.5: We know this when the learner talks about a picture, photograph or object:
Assessment Standard 2.10: We know this when the learner participates in a conversation on a familiar topic:
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment, and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts;
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner recognises and makes meaning of letters and words;awareness:
3.3.1 recognises on sight an increasing number of high-frequency words;
Assessment Standard 3.8: We know this when the learner reads on own for information and enjoyment:
3.8.4 distinguishes between fiction an non-fiction;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner will be able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.1: We know this when the learner writes individual words such as labels:
Assessment Standard 4.3: We know this when the learner spells common words correctly:
Assessment Standard 4.10: We know this when the learner with support, writes a short story dialogue:
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.5: We know this when the learner keeps a personal dictionary and uses a children’s dictionary:
Assessment Standard 5.7: We know this when the learner transfers information from one mode to another:
5.7.3 uses information from a chart, bar graph, diagram, mind map or picture to write or complete a short text.
Learning Outcome 6: GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY : The learner knows and is able to use the sounds, vocabulary and grammar of the language to create and interpret texts.
Assessment Standard 6.6: We know this when the learner understands some adjectives (e.g. bored, tired).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 3' conversation and receive update notifications?