| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
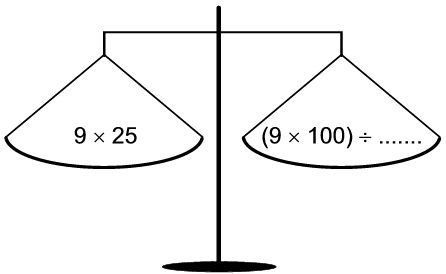
1.1 9 x 25 ÷9 x 100) ÷ 4
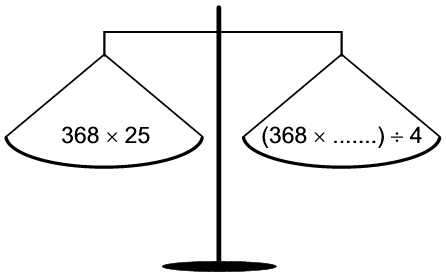
1.2 368 x 25 ÷368 x 100) ÷ 4
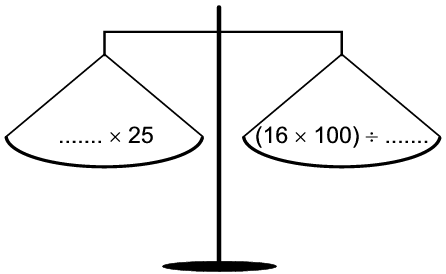
1.3 16 x 25 ÷16 x 100) ÷ 4
2. 2.1 ÷324 x 100) ÷ 4
32 400 ÷ 4
8 100
2.2 ÷1 436 x 100) ÷ 4
143 600 ÷ 4
35 900
2.3 ÷26 844 x 100) ÷ 4
2 684 400 ÷ 4
671 100
yes
÷1 436 ÷ 4) x 100
359 x 100
35 900
3.1
| 375 | |
| 625 | |
| 1 125 |
3.2
| 3 000 | _______ | 375 | |
| 5 000 | _______ | 625 | |
| 9 000 | _______ | 1 125 |
4. Answer the same.
5. 1 000
8
divide
8
1 000
multiplication
6.1 36 x 1 000 1 056 000 ÷ 8
36 000 132 000
6.2 132 x 1 000 ÷1 056 x 1 000 ÷ 8
132 000 132 000
x 1 000 2 / x 5 x 100 / 2 x 1 000
It is very important to develop strategies for arriving at answers quickly to make life easier in Grade 6. Let us take a look at some bright ideas to use when we do multiplication!
REMEMBER!
When you multiply by 25 you can first multiply by 100 and
then divide by 4!
1. Can you balance the following scales by filling in the correct number?
1.1
1.3
2. Use the above method to calculate:
2.1 324 x 25 =
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
2.2 1 436 x 25 =
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
2.3 26 844 x 25 =
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
BRAIN-TEASER!
Can I also first divide by 4 and then multiply by 100? _________________________
Prove your answer!
1 436 x 25 =_____________________________________
=___________________________________________
=___________________________________________
3. Look carefully at the following example and then complete the tables:
| 3.1 | 1 × 125 | 125 |
| 3 × 125 | _____ | |
| 5 × 125 | _____ | |
| 9 × 125 | _____ |
| 3.2 | 1 × 1 000 | 1 000 | ÷ 8 | 25 |
| 3 × 1 000 | _____ | ÷ 8 | _____ | |
| 5 × 1 000 | _____ | 8 | _____ | |
| 9 × 1 000 | _____ | 4 | _____ |
4. Compare the answers in the tables. What do you realise?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
5. Complete the following:
REMEMBER:
If I have to multiply by 125 I can first multiply by ____________________________
and then __________________ the answer I get by ___________________________
OR I can first divide the number by_________________________________ and then
____________________________ the answer by _____________________________
6. See if you can apply this method!
6.1 288 x 125 = ÷288 8) x 1 000
= _______________________
= _______________________
or
288 x 125 = ÷288 x 1 000) ÷ 8
= _______________________
= _______________________
6.2 1 056 x 125 = ÷1 056 ÷ 8) x 1 000 or _____________________
= _______________________
= _______________________
BRAIN-TEASER!
WITHOUT using a calculator, how would you multiply a number by 500 in two seconds?
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.10: We know this when the learner uses a range of techniques to perform written and mental calculations with whole numbers including:
1.10.3: building up and breaking down numbers.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.
Assessment Standard 2.3: We know this when the learner determines output values for given input values, or input values for given output values, using:
2.3.3: tables.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 6' conversation and receive update notifications?