| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Grade 3 learners continue to expand their vocabulary by listening and reading a variety of texts such as poem, stories, riddles and doing word puzzles.
These modules consolidate and revise the vocabulary and phonics introduced in Grade 2. More opportunities are given for written work producing longer texts of more varied kinds. Learners should not be afraid to make mistakes as the building of confidence and fluency should take priority above perfect written work.
Time scheduled for the modules
All learners should work through all eight modules as the phonics and spelling requirements are spread over these modules. The educator should however allow learners to complete them at their own pace namely ± two modules per term.
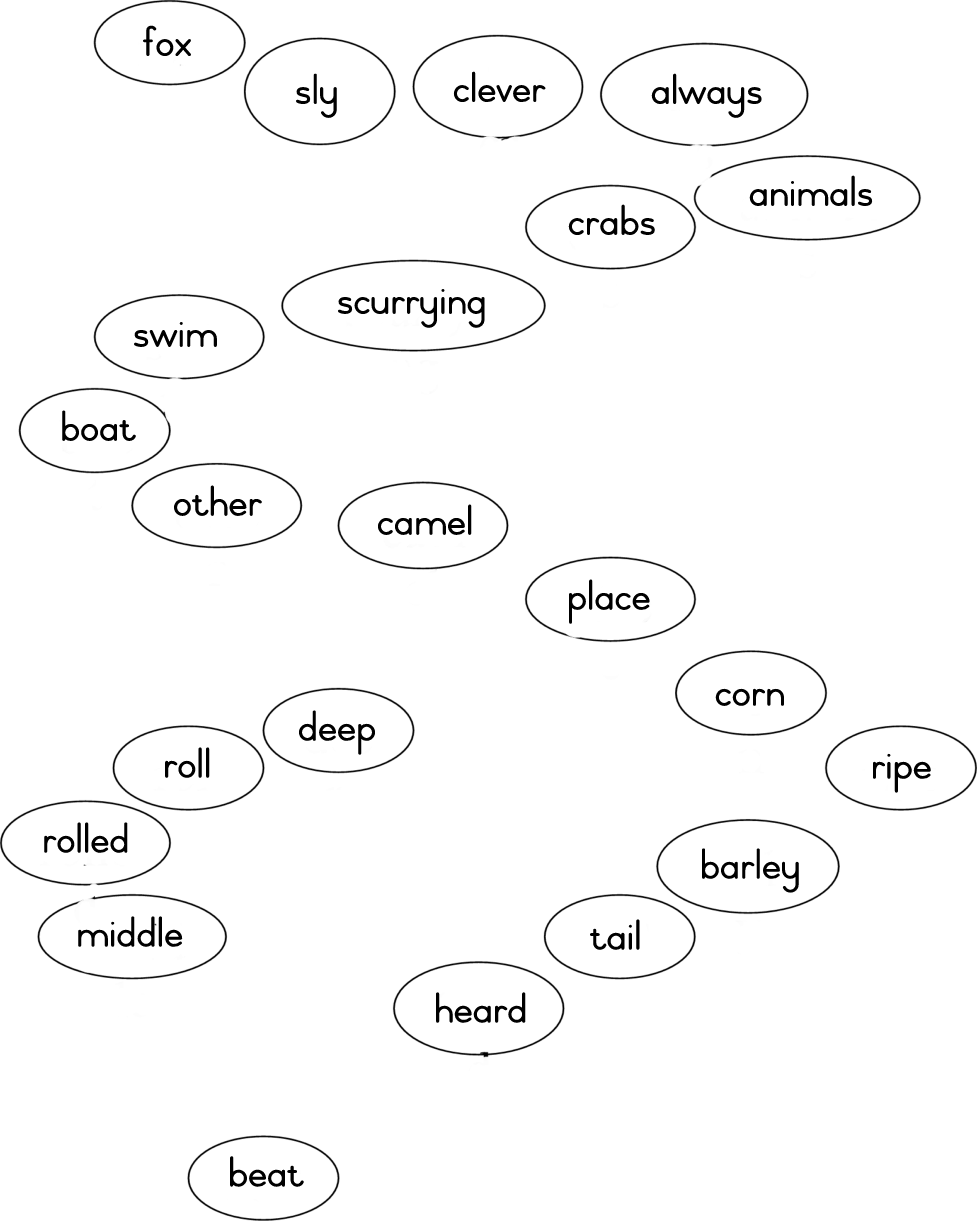
The story of “The Sly Old Fox” gives learners the opportunity to discuss such moral issues as honesty, truthfulness and faithfulness.
Learners write the dialogue between the characters.
A graph is kept for recording results of future spelling tests.
They read a factual article on crabs and make up their own story stimulated by a picture.
Integration of themes
We have a responsibility towards our friends. We need to be loyal, honest and helpful.
The fox did not even get the tip of his tail wet.
When they got to the other side the fox showed the camel the way to the ripe corn fields and the green, green barley.
The camel started eating the ripe corn and the green barley.
The fox ran back to the river.
He ate the big fat crabs on the soft sand.
He ate many big fat crabs.

| LO 3.3.1 | LO 3.4 |
When the fox had eaten as many crabs as he could he wanted to go home.

So the fox lay down on the sand and sang a little song.
He sang,
Somebody is eating your corn. Whoooooo!
Somebody is eating your barley. Whoooooo!
Whoooooo! Whoooooo! Whoooooo!
The farmer heard the song.
He ran out to the field to catch the fox.
But the fox hid behind the trees.
The farmer saw the camel in his field.
He beat him with sticks.
He chased him out of the field.
| LO 2.6.2 | LO 3.1.1 | LO 3.3.1 |
The fox found the camel lying on the sand.
“What happened to you, my friend?”
Asked the fox.
“Why did you sing that song?” asked the camel. “The farmer came and beat me with sticks!”
“Oh!" said the fox.
“I always sing after dinner.”
“Let’s go home,” said the camel. He was very cross. “Jump on my back. I will take you across the river.”
The fox climbed on his back. Not even the tip of his tail got wet.
When they came to the middle of the river where the water was deep, the camel said, “Now I must roll over. I always roll over after dinner.”

| LO 1.1.1 | LO 2.5 | LO 3.4 |
So the camel rolled over in the water.
The fox’s tail got wet.
His body got wet.
His head got wet.
His nose got wet.
Soon the sly old fox was wet all over.
And that was the end of the sly old fox.

cow

calf

sheep

lamb

porcupine

hen

chicks

fox
| LO 1.1.4 | LO 3.2.4 | LO 3.3.1 |
| LO 1.4 | LO 3.3.1 |
| LO 1.5.1 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner will be able to listen for information and enjoyment, and respond appropriately and critically in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner shows understanding of stories:
1.1.1 predicts what the story will be about from the title;
1.1.4 recalls and retells parts of the story;
Assessment Standard 1.4: We know this when the learner shows understanding of a sequence of instructions by following them correctly:
Assessment Standard 1.5: We know this when the learner develops phonic awareness:
1.5.1 distinguishes between different vowel sounds that are important for reading and writing (e.g. ‘u’ and ‘ur’ in ‘hut’ and ‘hurt’);
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.5: We know this when the learner talks about a picture, photograph or object:
Assessment Standard 2.6: We know this when the learner attends to pronunciation as part of reading, for example:
2.6.2 pays attention to pronunciation and intonation as part of communication;
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment, and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts;
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner uses visual cues to make meaning:
3.1.1 understands a picture story or comic strip by relating captions and speech bubbles to visual images;
Assessment Standard 3.2: We know this when the learner makes meaning of written text by reading with the teacher:
3.2.4 describes how the story makes self feel;
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner recognises and makes meaning of letters and words;awareness:
3.3.1 recognises on sight an increasing number of high-frequency words;
Assessment Standard 3.4: We know this when the learner reads with increasing speed and fluency.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 3' conversation and receive update notifications?