| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The combination of hydrogen with another element produces a hydride, E x H y . The formal charge or oxidation state of the hydrogen in these compounds is dependant on the relative electronegativity of the element in question.
Hydrogen compounds with highly electropositive metals, i.e., those in which the metal has an electronegativity of less than 1.2, are ionic with the hydrogen having a s 2 configuration (H - ). Typical ionic metal hydrides are those of the Group 1 (IA) metals and the heavier Group 2 (IIA) metals.
The ionic radius of the hydride ion is in between that of fluoride and chloride and the same as oxide ( [link] ). As a consequence, in the solid state the hydride ion replicates that of a halide ion (e.g., Cl - ), and as such similar solid state structures are observed ( [link] ).
| Ion | Ionic radius (Å) |
| H - | 1.40 |
| F - | 1.36 |
| Cl - | 1.81 |
| O 2- | 1.40 |
| Metal | Hydride | Fluoride | Chloride |
| Li | 4.085 | 4.0173 | 5.129 |
| Na | 4.880 | 4.620 | 5.640 |
| K | 5.700 | 5.347 | 6.292 |
| Rb | 6.037 | 5.640 | 6.581 |
| Cs | 6.376 | 6.008 | 7.020 |
Unlike the halide ions that are soluble in water, the hydride ion reacts with water, [link] , and consequently NaH and CaH 2 are commonly used as drying agents. The liberation of hydrogen was used as a commercial source of hydrogen for small-scale applications.
The most common binary compounds of hydrogen are those in which hydrogen bonds have covalent bond character. The E-H bond is usually polar ranging from those in which the hydrogen is polarized positively (e.g., those with non-metals such as F, O, S, and C) to where it is negative (e.g., those with metals and metalloids such as B, Al, etc). Magnesium hydride is intermediate between covalent and ionic since it has a polymeric solid similar to AlH 3 , but reacts rapidly with water like ionic hydrides. [link] lists the important covalent hydrides of p-block elements. It should be noted that all organic hydrocarbons can be thought of as simply the hydrides of carbon!
| Group 13 | Group 14 | Group 15 | Group 16 | Group 17 |
| B 2 H 6 | C n H 2n+2 , C n H 2n , C n H 2n-2 | NH 3 , N 2 H 4 | H 2 O, H 2 O 2 | HF |
| (AlH 3 ) n | Si n H 2n+2 | PH 3 , P 2 H 4 | H 2 S, H 2 S n | HCl |
| Ga 2 H 6 | Ge n H 2n+2 | AsH 3 | H 2 Se | HBr |
| SnH 4 | SbH 3 | H 2 Te | HI |
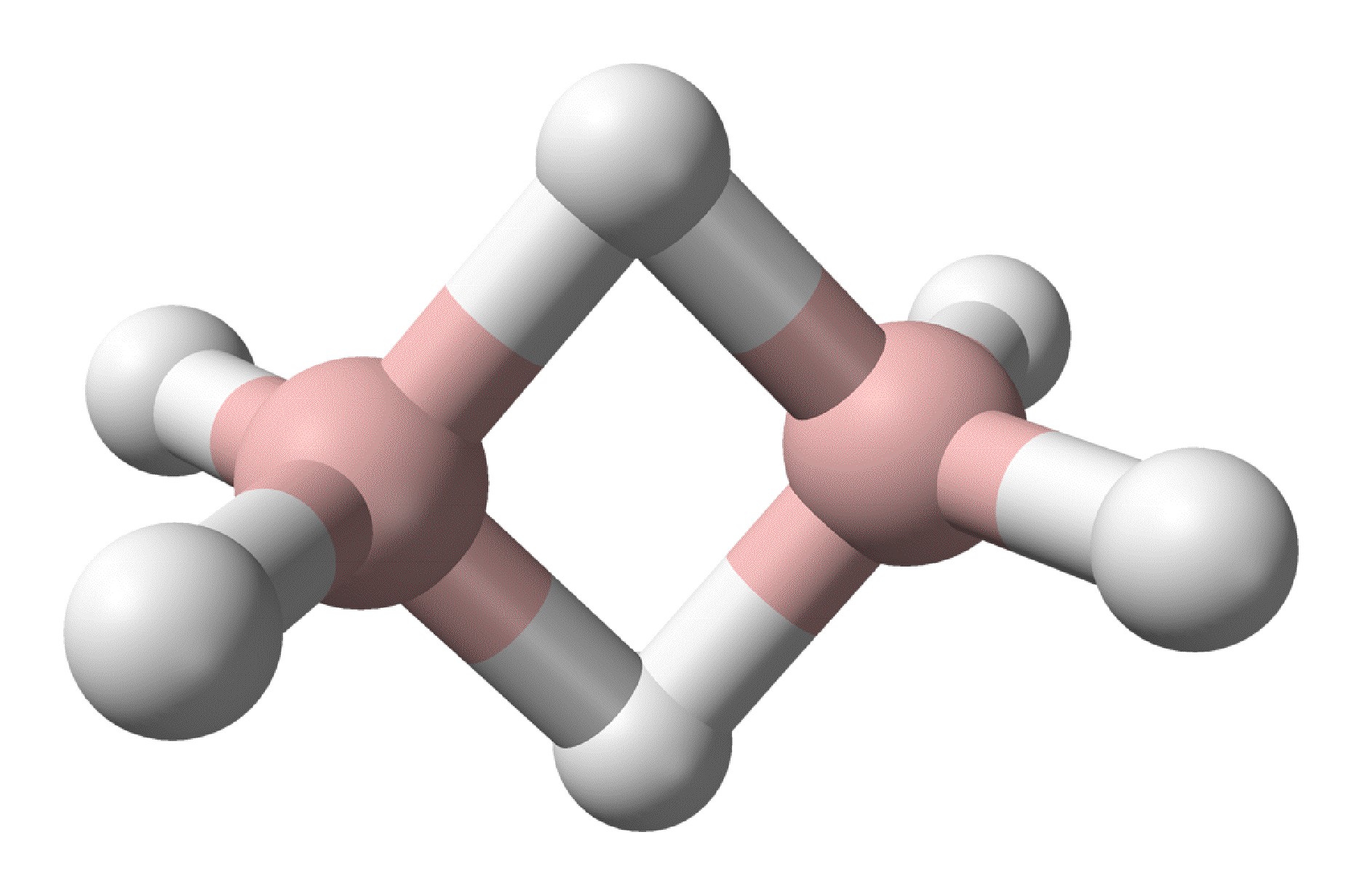
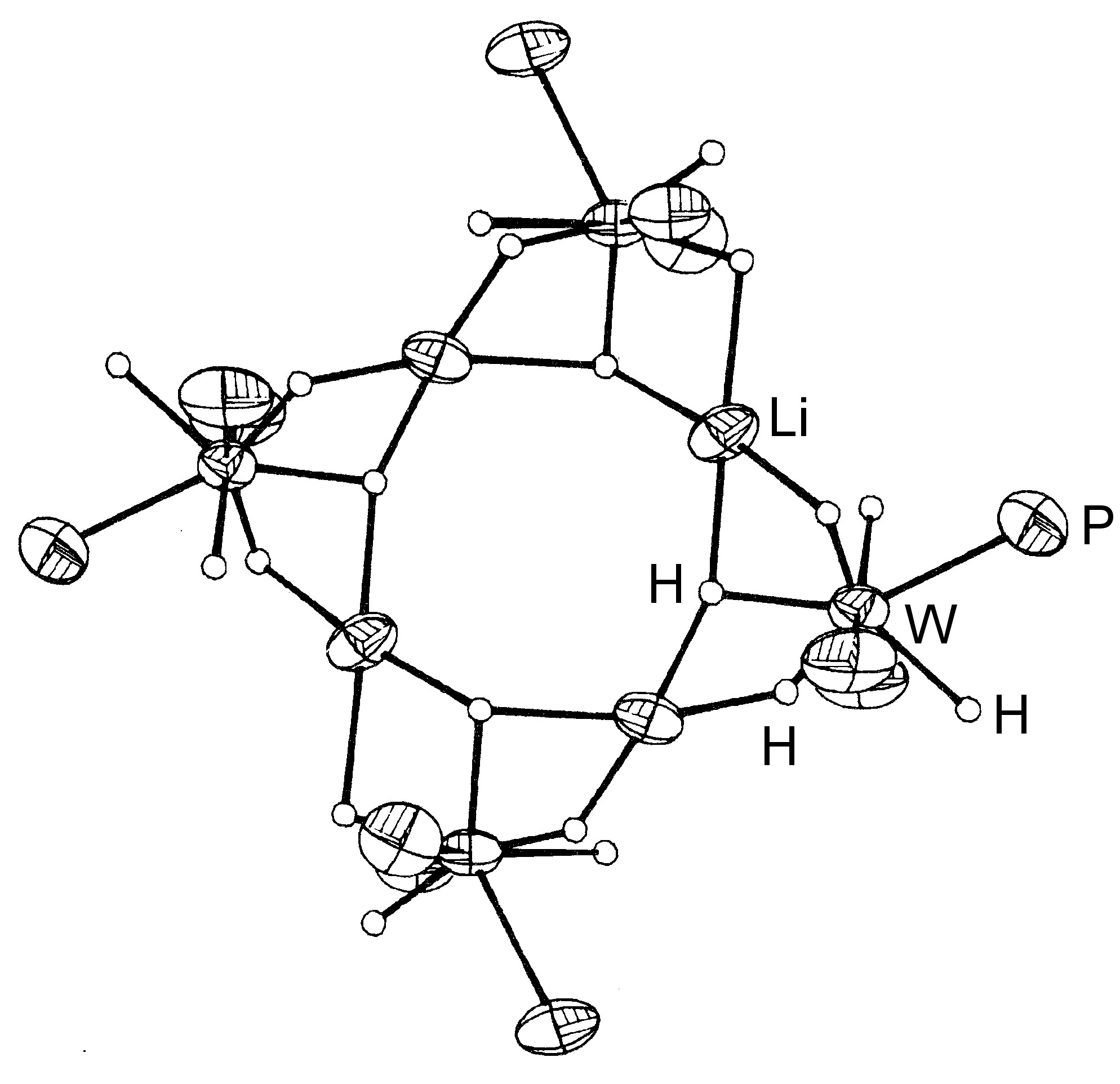
The elements of Group 14 to 17 all form hydrides with normal covalent bonds in which the hydrogen is bonded by a single bond to the element in question. In contrast, the elements of Group 13 (as typified by boron) all exhibit a second type of covalent bond: the electron deficient hydrogen bridged bond. In this type of bond the hydrogen nucleus is embedded in a molecular orbital that covers more than two atoms to create a multi-center two-electron bond. Diborane ( [link] ) represents the archetypal compound containing the hydrogen bridge bond. Hydrides are not limited to terminal (E-H) or those bridging two atoms (E-H-E), but are also known where the hydrogen bridges (or caps) more than two atoms, i.e., [link] .
Covalent hydrides can be made by a range of synthetic routes. The simplest is direct combination of the elements (in a similar manner to that used with ionic hydrides).
The use of a hydride as a reagent to reduce a halide or oxide of the desired element.
Metal phosphides, carbides, silicides, and borides result in the formation of the hydride.
Hydride compounds can be interconverted in the presence of a catalyst, heat, or an electrical discharge. This is the basis of catalytic cracking of petroleum mixtures.
Many transition metal, lanthanides and actinides absorb hydrogen to give a metallic hydride which retain the properties of a metal, although the presence of hydrogen does result in embrittlement of the metal. As such these hydrides are best considered as alloys since they do not have defined stoichiometries. For example, vanadium absorbs hydrogen to form an alloy with a maximum hydrogen content of VH 1.6 . In a similar manner palladium forms PdH 0.6 . The hydrogen atoms are present in interstitial sites in the metal’s lattice; hence interstitial hydride . Interstitial hydrides show certain promise as a way for safe hydrogen storage.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?