| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The proton, H + , is the name given to hydrogen in the +1 oxidation state.
The proton can be formed from the photolysis of atomic hydrogen in the vapor phase at low pressure.
The proton is more reactive than the hydrogen atom because of its high charge density. In addition, the proton’s small ionic radius, 1.5 x 10 -15 cm, means that it can get close to other atoms and hence form strong bonds.
The strength of the bonding interaction is such that it is very hard to measure directly. Instead the relative bond strength between the proton and an appropriate base, B 1 , is measured in the presence of a competing base, B 2 .
In measuring the exchange reaction, the relative proton affinity of B 1 and B 2 is measured. This is also known as the gas phase acidity, and as such it is a measure of the inherent acidity of a species X-H because it obviates any solvent effects.
The high reactivity of the proton means that it does not exist free in solution. There are however many H + containing species. These are generally classified as acids .
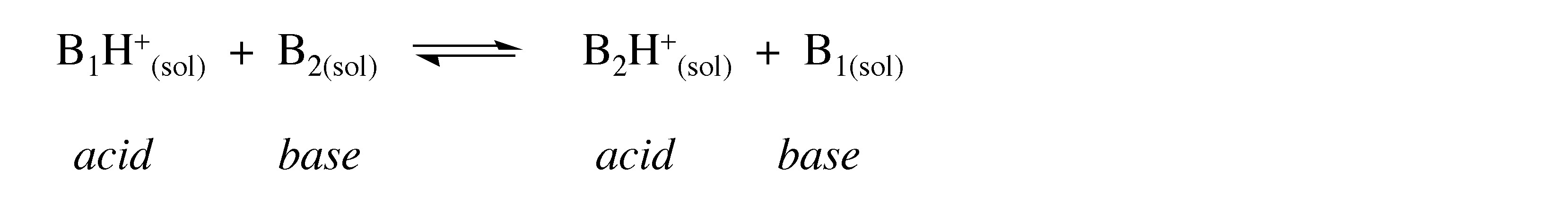
The reaction between the acid and the base is a proton transfer reaction. While the proton travels from B 1 to B 2 , it is never free in solution. Instead a bridged transition state or intermediate is formed, B 1 … H +… B 2 .
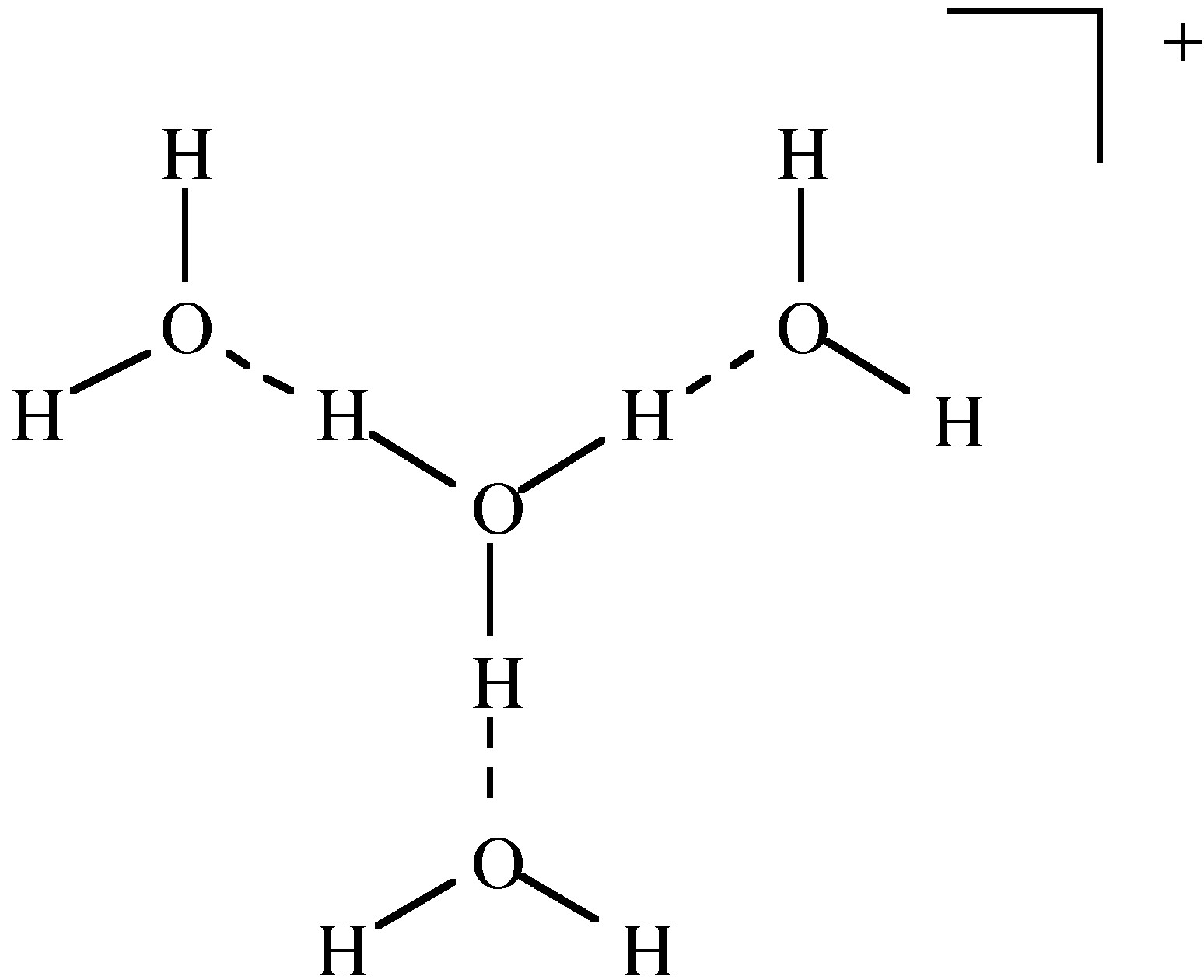
The most common solvent for H + is water. The acid form is usually defined as the hydronium ion or H 3 O + , [link] . The terms oxonium, hydroxonium and oxidanium are also used for the H 3 O + . Although we commonly use H 3 O + it is known from spectroscopy that larger complexes are formed such as H 9 O 4 + ( [link] ).
Acids and bases have been characterized in a number of different ways. In 1680 Robert Boyle ( [link] ) defined an acid as a compound that dissolved many other compounds, had a sour taste, and reacted with alkali (base).

Boyle’s simple observational description was rationalized by Danish physical chemist Johannes Brønsted ( [link] ). Brønsted proposed that acids are proton donors , and bases are proton acceptors . An acid-base reaction is one in which a proton is transferred from a proton donor (acid) to a proton acceptor (base). Based upon Brønsted’s proposal simple acids contain an ionizable proton. Examples of simple acids include neutral molecules (HCl, H 2 SO 4 ), anions (HSO 4 - , H 2 PO 4 - ), and cations (NH 4 + ). The most common Brønsted bases include metal hydroxides (MOH).

Brønsted noted that when an acid donates a proton it forms a conjugate base. The following are examples of an acid and its conjugate base.



What is the conjugate base of [Al(H 2 O) 6 ] 3+ ?
[Al(H 2 O) 5 (OH)] 2+
The same occurs when a base accepts a proton it forms a conjugate acid. The following are examples of a base and its conjugate acid.



Thus, the reaction between an acid and a base results in the formation of the appropriate conjugate base and conjugate acid.
A specific example is as follows:
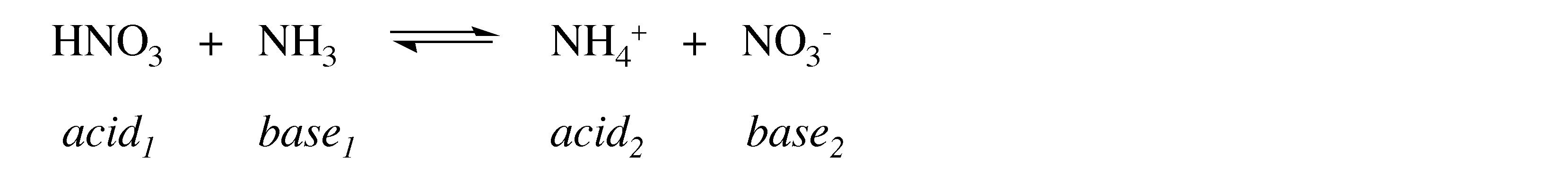
What is the conjugate acid and base formed from the reaction of NH 4 + with S 2- ?
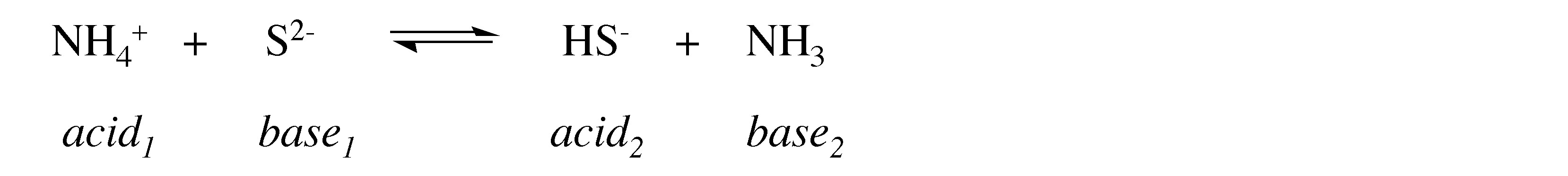
In the equilibrium reactions shown in [link] and [link] there is a competition between the two bases for the proton. As would be expected the strongest base wins.
When a strong acid is added to (dissolved in) water it will react with the water as a base:
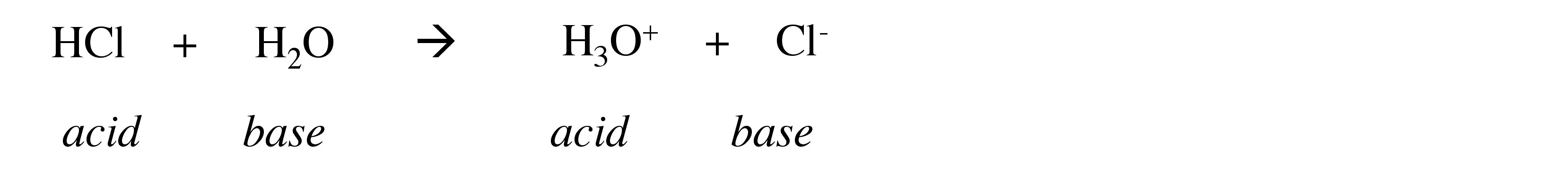
In contrast, when a strong base is added to (dissolved in) water it will react with the water as an acid:
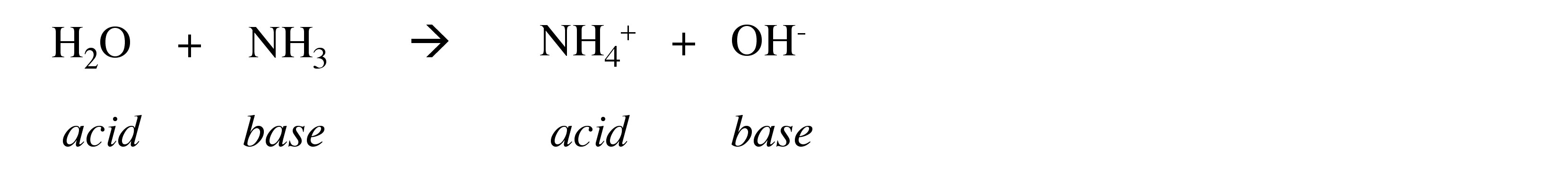
The acidity of a water (aqueous) solution depends on the concentration of the hydronium ion, i.e., [H 3 O + ]. The acidity of a solution is therefore the ability of the solution to donate a proton to a base. The acidity or pH of a solution is defined as:
It is important to note that the value is the activity of H 3 O + and not the concentration .
The activity of the H 3 O + ion can be measured by
The proton transfer reaction is one of the simplest reactions in chemistry. It involves no electrons and low mass transfer/change, giving it a low energy of activation. For proton transfer between O-H or N-H groups and their associated bases the reaction is very fast. The proton transfer occurs across a hydrogen-bonded pathway during which the proton is never free.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?