| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the preceding section, we used definite integrals to find the area between two curves. In this section, we use definite integrals to find volumes of three-dimensional solids. We consider three approaches—slicing, disks, and washers—for finding these volumes, depending on the characteristics of the solid.
Just as area is the numerical measure of a two-dimensional region, volume is the numerical measure of a three-dimensional solid. Most of us have computed volumes of solids by using basic geometric formulas. The volume of a rectangular solid, for example, can be computed by multiplying length, width, and height: The formulas for the volume of a sphere a cone and a pyramid have also been introduced. Although some of these formulas were derived using geometry alone, all these formulas can be obtained by using integration.
We can also calculate the volume of a cylinder. Although most of us think of a cylinder as having a circular base, such as a soup can or a metal rod, in mathematics the word cylinder has a more general meaning. To discuss cylinders in this more general context, we first need to define some vocabulary.
We define the cross-section of a solid to be the intersection of a plane with the solid. A cylinder is defined as any solid that can be generated by translating a plane region along a line perpendicular to the region, called the axis of the cylinder. Thus, all cross-sections perpendicular to the axis of a cylinder are identical. The solid shown in [link] is an example of a cylinder with a noncircular base. To calculate the volume of a cylinder, then, we simply multiply the area of the cross-section by the height of the cylinder: In the case of a right circular cylinder (soup can), this becomes
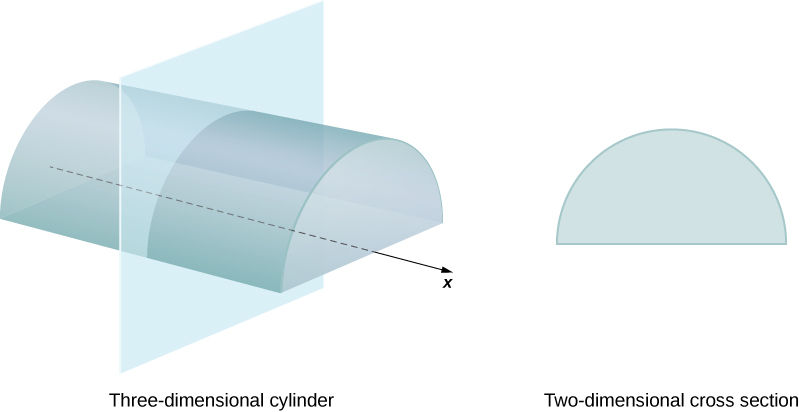
If a solid does not have a constant cross-section (and it is not one of the other basic solids), we may not have a formula for its volume. In this case, we can use a definite integral to calculate the volume of the solid. We do this by slicing the solid into pieces, estimating the volume of each slice, and then adding those estimated volumes together. The slices should all be parallel to one another, and when we put all the slices together, we should get the whole solid. Consider, for example, the solid S shown in [link] , extending along the
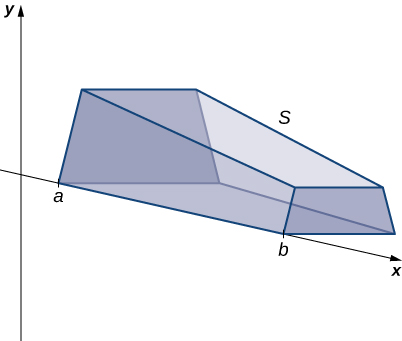
We want to divide into slices perpendicular to the As we see later in the chapter, there may be times when we want to slice the solid in some other direction—say, with slices perpendicular to the y -axis. The decision of which way to slice the solid is very important. If we make the wrong choice, the computations can get quite messy. Later in the chapter, we examine some of these situations in detail and look at how to decide which way to slice the solid. For the purposes of this section, however, we use slices perpendicular to the

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?