| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The purpose of this chapter is to describe motion, and now that we understand the definitions of displacement, distance, velocity, speed and acceleration, we are ready to start using these ideas to describe how an object is moving. There are many ways of describing motion:
These methods will be described in this section.
We will consider three types of motion: when the object is not moving (stationary object), when the object is moving at a constant velocity (uniform motion) and when the object is moving at a constant acceleration (motion at constant acceleration).
The simplest motion that we can come across is that of a stationary object. A stationary object does not move and so its position does not change, for as long as it is standing still. An example of this situation is when someone is waiting for something without moving.The person remains in the same position.
Lesedi is waiting for a taxi. He is standing two metres from a stop street at = 0 s. After one minute, at = 60 , he is still 2 metres from the stop street and after two minutes, at = 120 , also 2 metres from the stop street. His position has not changed. His displacement is zero (because his position is the same), his velocity is zero (because his displacement is zero) and his acceleration is also zero (because his velocity is not changing).
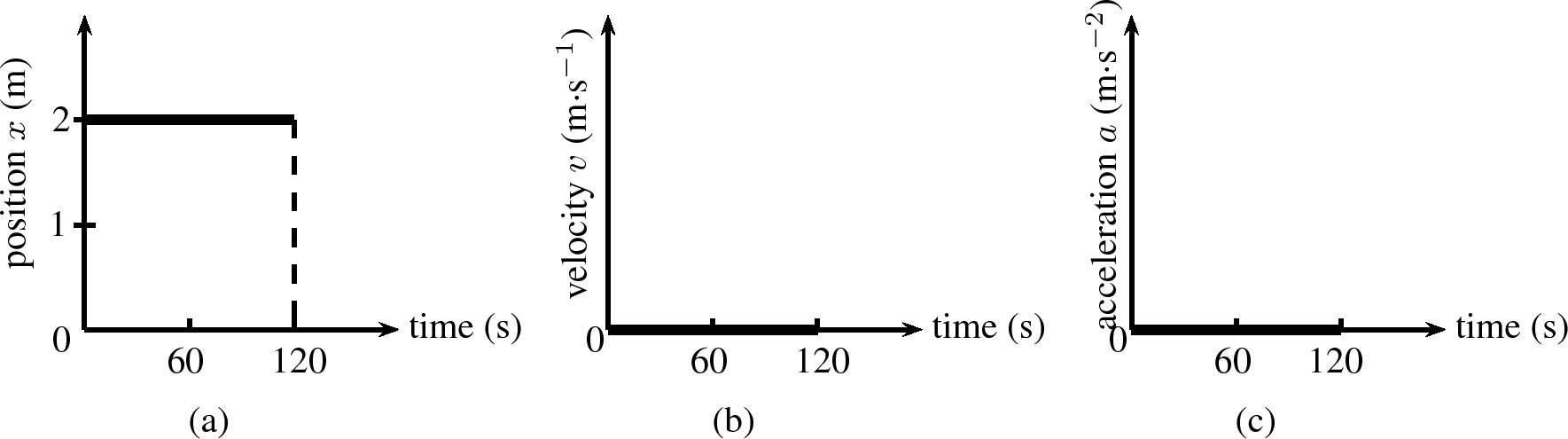
We can now draw graphs of position vs. time ( vs. ), velocity vs. time ( vs. ) and acceleration vs. time ( vs. ) for a stationary object. The graphs are shown in [link] . Lesedi's position is 2 metres from the stop street. If the stop street is taken as the reference point, his position remains at 2 metres for 120 seconds. The graph is a horizontal line at 2 m.The velocity and acceleration graphs are also shown. They are both horizontal lines on the -axis. Since his position is not changing, his velocity is and since velocity is not changing, acceleration is .
The gradient of a line can be calculated by dividing the change in the -value by the change in the -value.
m =
Since we know that velocity is the rate of change of position, we can confirm the value for the velocity vs. time graph, by calculating the gradient of the vs. graph.
If we calculate the gradient of the vs. graph for a stationary object we get:
Similarly, we can confirm the value of the acceleration by calculating the gradient of the velocity vs. time graph.
If we calculate the gradient of the vs. graph for a stationary object we get:
Additionally, because the velocity vs. time graph is related to the position vs. time graph, we can use the area under the velocity vs. time graph to calculate the displacement of an object.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 physical science [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?