| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Displacement is the change in an object's position.
The displacement of an object is defined as its change in position (final position minus initial position). Displacement has a magnitude and direction and is therefore a vector. For example, if the initial position of a car is and it moves to a final position of , then the displacement is:
However, subtracting an initial quantity from a final quantity happens often in Physics, so we use the shortcut to mean final - initial . Therefore, displacement can be written:
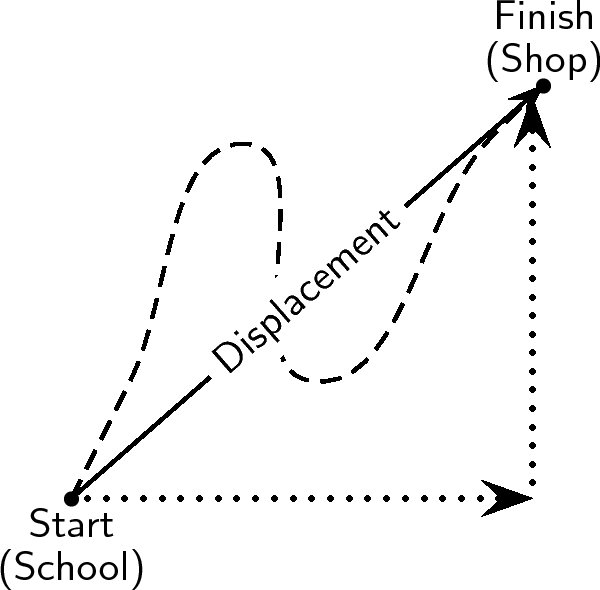
Displacement does not depend on the path travelled, but only on the initial and final positions ( [link] ). We use the word distance to describe how far an object travels along a particular path. Distance is the actual distance that was covered. Distance (symbol ) does not have a direction, so it is a scalar. Displacement is the shortest distance from the starting point to the endpoint – from the school to the shop in the figure. Displacement has direction and is therefore a vector.
[link] shows the five houses we discussed earlier. Jack walks to school, but instead of walking straight to school, he decided to walk to his friend Joel's house first to fetch him so that they can walk to school together. Jack covers a distance of to Joel's house and another to school. He covers a distance of . His displacement, however, is only towards the school. This is because displacement only looks at the starting position (his house) and the end position (the school). It does not depend on the path he travelled.
To calculate his distance and displacement, we need to choose a reference point and a direction. Let's choose Jack's house as the reference point, and towards Joel's house as the positive direction (which means that towards the school is negative). We would do the calculations as follows:
Joel walks to school with Jack and after school walks back home. What is Joel's displacement and what distance did he cover? For this calculation we use Joel's house as the reference point. Let's take towards the school as the positive direction.
It is possible to have a displacement of and a distance that is not . This happens when an object completes a round trip back to its original position, like an athlete running around a track.
Very often in calculations you will get a negative answer. For example, Jack's displacement in the example above, is calculated as . The minus sign in front of the answer means that his displacement is in the opposite direction (opposite to the direction chosen as positive in the beginning of the question). When we start a calculation we choose a frame of reference and a positive direction. In the first example above, the reference point is Jack's house and the positive direction is towards Joel's house. Therefore Jack's displacement is towards the school. Notice that distance has no direction, but displacement has.
The differences between distance and displacement can be summarised as:
| Distance | Displacement |
| 1. depends on the path | 1. independent of path taken |
| 2. always positive | 2. can be positive or negative |
| 3. is a scalar | 3. is a vector |
| 4. does not have a direction | 4. has a direction |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 physical science [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?