| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The process by which an organism develops from a single-celled zygote to a multi-cellular organism is complex and well regulated. The regulation occurs through signaling between cells and tissues and responses in the form of differential gene expression.
Fertilization is the process in which gametes (an egg and sperm) fuse to form a zygote ( [link] ). To ensure that the offspring has only one complete diploid set of chromosomes, only one sperm must fuse with one egg. In mammals, a layer called the zona pellucida protects the egg. At the tip of the head of a sperm cell is a structure like a lysosome called the acrosome, which contains enzymes. When a sperm binds to the zona pellucida, a series of events, called the acrosomal reactions, take place. These reactions, involving enzymes from the acrosome, allow the sperm plasma membrane to fuse with the egg plasma membrane and permit the sperm nucleus to transfer into the ovum. The nuclear membranes of the egg and sperm break down and the two haploid nuclei fuse to form a diploid nucleus or genome.
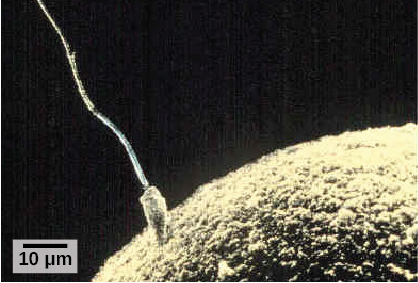
To ensure that no more than one sperm fertilizes the egg, once the acrosomal reactions take place at one location of the egg membrane, the egg releases proteins in other locations to prevent other sperm from fusing with the egg.
The development of multi-cellular organisms begins from this single-celled zygote, which undergoes rapid cell division, called cleavage ( [link] a ), to form a hollow ball of cells called a blastula ( [link] b ).
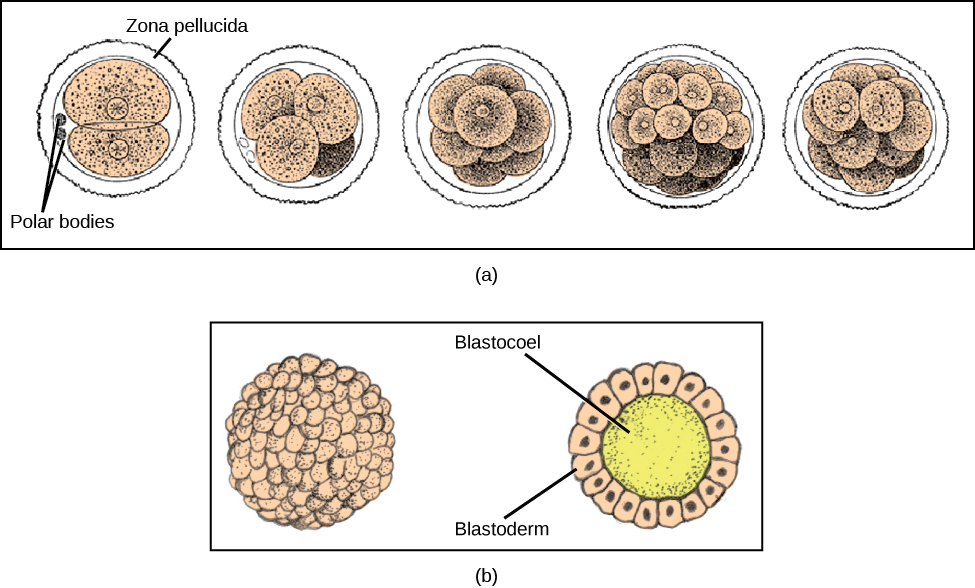
In mammals, the blastula forms the blastocyst in the next stage of development. Here the cells in the blastula arrange themselves in two layers: the inner cell mass , and an outer layer called the trophoblast . The inner cell mass will go on to form the embryo. The trophoblast secretes enzymes that allow implantation of the blastocyst into the endometrium of the uterus. The trophoblast will contribute to the placenta and nourish the embryo.
Visit the Virtual Human Embryo project at the Endowment for Human Development site to click through an interactive of the stages of embryo development, including micrographs and rotating 3-D images.
The cells in the blastula then rearrange themselves spatially to form three layers of cells. This process is called gastrulation . During gastrulation, the blastula folds in on itself and cells migrate to form the three layers of cells ( [link] ) in a structure, the gastrula, with a hollow space that will become the digestive tract. Each of the layers of cells is called a germ layer and will differentiate into different organ systems.
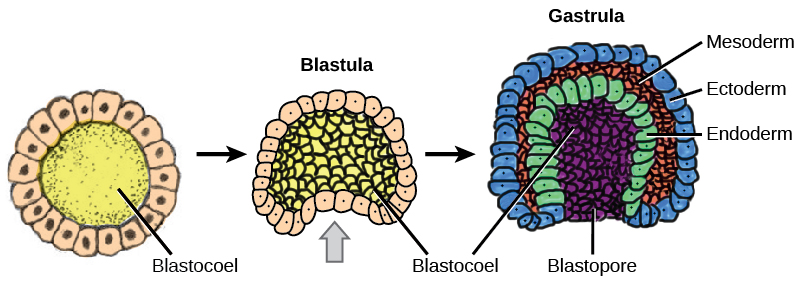
The three germ layers are the endoderm, the ectoderm, and the mesoderm. Cells in each germ layer differentiate into tissues and embryonic organs. The ectoderm gives rise to the nervous system and the epidermis, among other tissues. The mesoderm gives rise to the muscle cells and connective tissue in the body. The endoderm gives rise to the gut and many internal organs.
Gastrulation leads to the formation of the three germ layers that give rise during further development to the different organs in the animal body. This process is called organogenesis .
Organs develop from the germ layers through the process of differentiation. During differentiation, the embryonic stem cells express specific sets of genes that will determine their ultimate cell type. For example, some cells in the ectoderm will express the genes specific to skin cells. As a result, these cells will take on the shape and characteristics of epidermal cells. The process of differentiation is regulated by location-specific chemical signals from the cell’s embryonic environment that sets in play a cascade of events that regulates gene expression.
The early stages of embryonic development begin with fertilization. The process of fertilization is tightly controlled to ensure that only one sperm fuses with one egg. After fertilization, the zygote undergoes cleavage to form the blastula. The blastula, which in some species is a hollow ball of cells, undergoes a process called gastrulation, during which the three germ layers form. The ectoderm gives rise to the nervous system and the epidermal skin cells, the mesoderm gives rise to the muscle cells and connective tissue in the body, and the endoderm gives rise to the digestive system and other internal organs. Organogenesis is the formation of organs from the germ layers. Each germ layer gives rise to specific tissue types.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bccampus - concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?