| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It is quite difficult to qualitatively analyze the Laplace transform and Z-transform , since mappings of their magnitude and phase or real part andimaginary part result in multiple mappings of 2-dimensional surfaces in 3-dimensional space. For this reason, it is verycommon to examine a plot of a transfer function's poles and zeros to try to gain a qualitative idea of what a system does.
Once the Laplace-transform of a system has been determined, one can use the information contained in function's polynomials tographically represent the function and easily observe many defining characteristics. The Laplace-transform will have the belowstructure, based on Rational Functions :
The two polynomials, and , allow us to find the poles and zeros of the Laplace-Transform.
Below is a simple transfer function with the poles and zeros shown below it.
The zeros are:
The poles are:
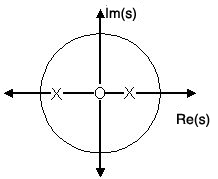
Once the poles and zeros have been found for a given Laplace Transform, they can be plotted onto the S-Plane. TheS-plane is a complex plane with an imaginary and real axis referring to the complex-valued variable . The position on the complex plane is given by and the angle from the positive, real axis around the plane is denoted by . When mapping poles and zeros onto the plane, poles are denoted byan "x" and zeros by an "o". The below figure shows the S-Plane, and examples of plotting zeros and poles onto theplane can be found in the following section.

This section lists several examples of finding the poles and zeros of a transfer function and then plotting them onto the S-Plane.
The zeros are:
The poles are:
The zeros are:
The poles are:

An easy mistake to make with regards to poles and zeros is to think that a function like is the same as . In theory they are equivalent, as the pole and zero at cancel each other out in what is known as pole-zero cancellation . However, think about what may happen if this were a transfer function of a system that wascreated with physical circuits. In this case, it is very unlikely that the pole and zero would remain in exactly thesame place. A minor temperature change, for instance, could cause one of them to move just slightly. If this were tooccur a tremendous amount of volatility is created in that area, since there is a change from infinity at the pole tozero at the zero in a very small range of signals. This is generally a very bad way to try to eliminate a pole. A muchbetter way is to use control theory to move the pole to a better place.
MATLAB - If access to MATLAB is readily available, then you can use its functions to easily createpole/zero plots. Below is a short program that plots the poles and zeros from the above example onto the Z-Plane.
% Set up vector for zerosz = [j ; -j];% Set up vector for poles
p = [-1 ; .5+.5j ; .5-.5j];
figure(1);zplane(z,p);
title('Pole/Zero Plot for Complex Pole/Zero Plot Example');
Now that we have found and plotted the poles and zeros, we must ask what it is that this plot gives us. Basically whatwe can gather from this is that the magnitude of the transfer function will be larger when it is closer to the poles andsmaller when it is closer to the zeros. This provides us with a qualitative understanding of what the system does at variousfrequencies and is crucial to the discussion of stability .
The region of convergence (ROC) for in the complex Z-plane can be determined from the pole/zero plot.Although several regions of convergence may be possible, where each one corresponds to a different impulse response, thereare some choices that are more practical. A ROC can be chosen to make the transfer function causal and/or stable dependingon the pole/zero plot.

The reason it is helpful to understand and create these pole/zero plots is due to their ability to help us easilydesign a filter. Based on the location of the poles and zeros, the magnitude response of the filter can be quicklyunderstood. Also, by starting with the pole/zero plot, one can design a filter and obtain its transfer function veryeasily.
Pole-Zero Plots are clearly quite useful in the study of the Laplace and Z transform, affording us a method of visualizing the at times confusing mathematical functions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?