| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
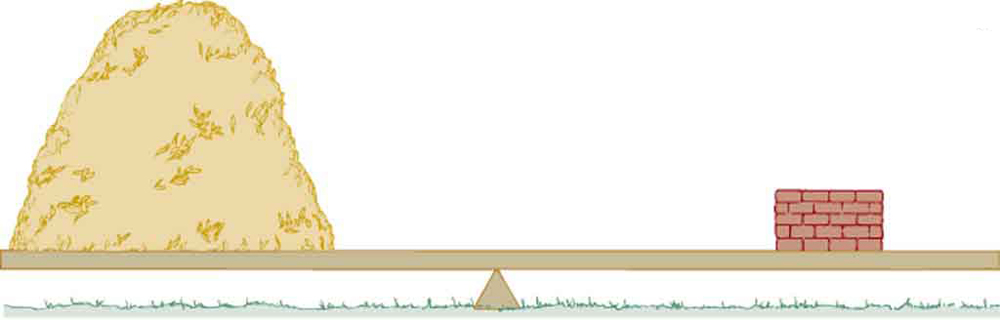
Which weighs more, a ton of feathers or a ton of bricks? This old riddle plays with the distinction between mass and density. A ton is a ton, of course; but bricks have much greater density than feathers, and so we are tempted to think of them as heavier. (See [link] .)
Density , as you will see, is an important characteristic of substances. It is crucial, for example, in determining whether an object sinks or floats in a fluid. Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance or object. In equation form, density is defined as
where the Greek letter (rho) is the symbol for density, is the mass, and is the volume occupied by the substance.
Density is mass per unit volume.
where is the symbol for density, is the mass, and is the volume occupied by the substance.
In the riddle regarding the feathers and bricks, the masses are the same, but the volume occupied by the feathers is much greater, since their density is much lower. The SI unit of density is , representative values are given in [link] . The metric system was originally devised so that water would have a density of , equivalent to . Thus the basic mass unit, the kilogram, was first devised to be the mass of 1000 mL of water, which has a volume of 1000 cm 3 .
| Substance | Substance | Substance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solids | Liquids | Gases | |||
| Aluminum | 2.7 | Water (4ºC) | 1.000 | Air | |
| Brass | 8.44 | Blood | 1.05 | Carbon dioxide | |
| Copper (average) | 8.8 | Sea water | 1.025 | Carbon monoxide | |
| Gold | 19.32 | Mercury | 13.6 | Hydrogen | |
| Iron or steel | 7.8 | Ethyl alcohol | 0.79 | Helium | |
| Lead | 11.3 | Petrol | 0.68 | Methane | |
| Polystyrene | 0.10 | Glycerin | 1.26 | Nitrogen | |
| Tungsten | 19.30 | Olive oil | 0.92 | Nitrous oxide | |
| Uranium | 18.70 | Oxygen | |||
| Concrete | 2.30–3.0 | Steam | |||
| Cork | 0.24 | ||||
| Glass, common (average) | 2.6 | ||||
| Granite | 2.7 | ||||
| Earth’s crust | 3.3 | ||||
| Wood | 0.3–0.9 | ||||
| Ice (0°C) | 0.917 | ||||
| Bone | 1.7–2.0 |
As you can see by examining [link] , the density of an object may help identify its composition. The density of gold, for example, is about 2.5 times the density of iron, which is about 2.5 times the density of aluminum. Density also reveals something about the phase of the matter and its substructure. Notice that the densities of liquids and solids are roughly comparable, consistent with the fact that their atoms are in close contact. The densities of gases are much less than those of liquids and solids, because the atoms in gases are separated by large amounts of empty space.
A pile of sugar and a pile of salt look pretty similar, but which weighs more? If the volumes of both piles are the same, any difference in mass is due to their different densities (including the air space between crystals). Which do you think has the greater density? What values did you find? What method did you use to determine these values?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics ii' conversation and receive update notifications?