| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
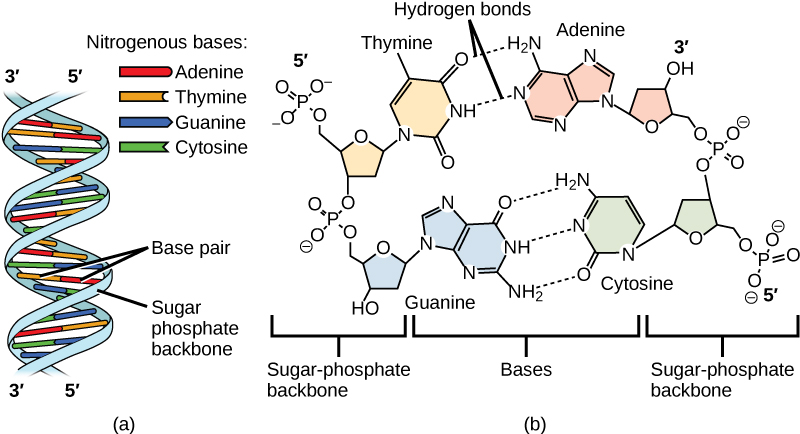
Watson and Crick proposed that the DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a right-handed helix, called a double helix . Base-pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine: namely, A pairs with T, and G pairs with C. In other words, adenine and thymine are complementary base pairs, and cytosine and guanine are also complementary base pairs. This is the basis for Chargaff’s rule; because of their complementarity, there is as much adenine as thymine in a DNA molecule and as much guanine as cytosine. Adenine and thymine are connected by two hydrogen bonds, and cytosine and guanine are connected by three hydrogen bonds. The two strands are anti-parallel in nature; that is, one strand will have the 3' carbon of the sugar in the “upward” position, whereas the other strand will have the 5' carbon in the upward position. The diameter of the DNA double helix is uniform throughout because a purine (two rings) always pairs with a pyrimidine (one ring) and their combined lengths are always equal. ( [link] ).
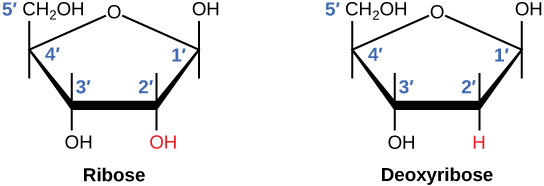
There is a second nucleic acid in all cells called ribonucleic acid, or RNA. Like DNA, RNA is a polymer of nucleotides. Each of the nucleotides in RNA is made up of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. In the case of RNA, the five-carbon sugar is ribose, not deoxyribose. Ribose has a hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon, unlike deoxyribose, which has only a hydrogen atom ( [link] ).
RNA nucleotides contain the nitrogenous bases adenine, cytosine, and guanine. However, they do not contain thymine, which is instead replaced by uracil, symbolized by a “U.” RNA exists as a single-stranded molecule rather than a double-stranded helix. Molecular biologists have named several kinds of RNA on the basis of their function. These include messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA)—molecules that are involved in the production of proteins from the DNA code.
DNA is a working molecule; it must be replicated when a cell is ready to divide, and it must be “read” to produce the molecules, such as proteins, to carry out the functions of the cell. For this reason, the DNA is protected and packaged in very specific ways. In addition, DNA molecules can be very long. Stretched end-to-end, the DNA molecules in a single human cell would come to a length of about 2 meters. Thus, the DNA for a cell must be packaged in a very ordered way to fit and function within a structure (the cell) that is not visible to the naked eye. The chromosomes of prokaryotes are much simpler than those of eukaryotes in many of their features ( [link] ). Most prokaryotes contain a single, circular chromosome that is found in an area in the cytoplasm called the nucleoid.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology for slcc biol 1010' conversation and receive update notifications?