| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The following graph shows the temperature throughout the month of March. Actually, I just made this graph up—the numbers do not actually reflect the temperature throughout the month of March. We’re just pretending, OK?
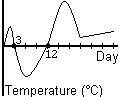
Give a weather report for the month of March, in words.
On what days was the temperature exactly 0°C?
On what days was the temperature below freezing?
On what days was the temperature above freezing?
What is the domain of this graph?
During what time periods was the temperature going up?
During what time periods was the temperature going down?
Mary started a company selling French Fries over the Internet. For the first 3 days, while she worked on the technology, she lost $100 per day. Then she opened for business. People went wild over her French Fries! She made $200 in one day, $300 the day after that, and $400 the day after that. The following day she was sued by an angry customer who discovered that Mary had been using genetically engineered potatoes. She lost $500 in the lawsuit that day, and closed up her business. Draw a graph showing Mary’s profits as a function of days.
Fill in the following table. Then draw graphs of the functions , , , , , and .
| -3 | ||||||
| -2 | ||||||
| -1 | ||||||
| 0 | ||||||
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | ||||||
| 3 |
Now describe in words what happened…

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Advanced algebra ii: activities and homework' conversation and receive update notifications?