| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Given the importance, in the area of high performance computing, of the performance of a computer’s memory subsystem, many techniques have been used to improve the performance of the memory systems of computers. The two attributes of memory system performance are generally bandwidth and latency . Some memory system design changes improve one at the expense of the other, and other improvements positively impact both bandwidth and latency. Bandwidth generally focuses on the best possible steady-state transfer rate of a memory system. Usually this is measured while running a long unit-stride loop reading or reading and writing memory. See the STREAM section in [link] Chapter 15 for measures of memory bandwidth. Latency is a measure of the worst-case performance of a memory system as it moves a small amount of data such as a 32- or 64-bit word between the processor and memory. Both are important because they are an important part of most high performance applications.
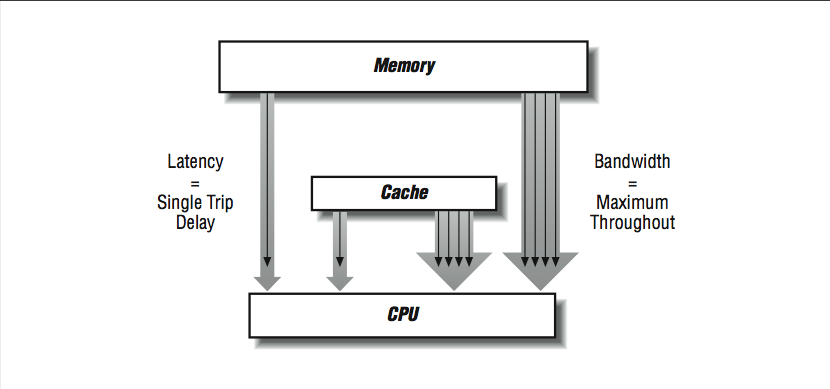
Because memory systems are divided into components, there are different bandwidth and latency figures between different components as shown in [link] . The bandwidth rate between a cache and the CPU will be higher than the bandwidth between main memory and the cache, for instance. There may be several caches and paths to memory as well. Usually, the peak memory bandwidth quoted by vendors is the speed between the data cache and the processor.
In the rest of this section, we look at techniques to improve latency, bandwidth, or both.
As we mentioned at the start of this chapter, the disparity between CPU speeds and memory is growing. If you look closely, you can see vendors innovating in several ways. Some workstations are being offered with 4- MB data caches! This is larger than the main memory systems of machines just a few years ago. With a large enough cache, a small (or even moderately large) data set can fit completely inside and get incredibly good performance. Watch out for this when you are testing new hardware. When your program grows too large for the cache, the performance may drop off considerably, perhaps by a factor of 10 or more, depending on the memory access patterns. Interestingly, an increase in cache size on the part of vendors can render a benchmark obsolete.
Simple memory system
Up to 1992, the Linpack 100×100 benchmark was probably the single most- respected benchmark to determine the average performance across a wide range of applications. In 1992, IBM introduced the IBM RS-6000 which had a cache large enough to contain the entire 100×100 matrix for the duration of the benchmark. For the first time, a workstation had performance on this benchmark on the same order of supercomputers. In a sense, with the entire data structure in a SRAM cache, the RS-6000 was operating like a Cray vector supercomputer. The problem was that the Cray could maintain and improve the performance for a 120×120 matrix, whereas the RS-6000 suffered a significant performance loss at this increased matrix size. Soon, all the other workstation vendors introduced similarly large caches, and the 100×100 Linpack benchmark ceased to be useful as an indicator of average application performance.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'High performance computing' conversation and receive update notifications?