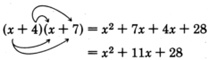This module is from Elementary Algebra by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr.
Factoring is an essential skill for success in algebra and higher level mathematics courses. Therefore, we have taken great care in developing the student's understanding of the factorization process. The technique is consistently illustrated by displaying an empty set of parentheses and describing the thought process used to discover the terms that are to be placed inside the parentheses.The factoring scheme for special products is presented with both verbal and symbolic descriptions, since not all students can interpret symbolic descriptions alone. Two techniques, the standard "trial and error" method, and the "collect and discard" method (a method similar to the "ac" method), are presented for factoring trinomials with leading coefficients different from 1.
Objectives of this module: be able to factor trinomials with leading coefficient 1, become familiar with some factoring hints.
Overview
Method
Let’s consider the product of the two binomials
and
.
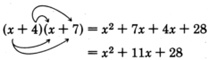
Notice that the
first term in the resulting trinomial comes from the product of the first terms in the binomials:
. The
last term in the trinomial comes from the product of the last terms in the binomials:
. The
middle term comes from the addition of the outer and inner products:
. Also, notice that the coefficient of the middle term is exactly the
sum of the last terms in the binomials:
.
The problem we’re interested in is that given a trinomial, how can we find the factors? When the leading coefficient (the coefficient of the quadratic term) is 1, the observations we made above lead us to the following method of factoring.
Method of factoring
- Write two sets of parentheses:
.
- Place a binomial into each set of parentheses. The first term of each binomial is a factor of the first term of the trinomial.
- Determine the second terms of the binomials by determining the factors of the third term that when added together yield the coefficient of the middle term.
Sample set a
Factor the following trinomials.
- Write two sets of parentheses:
.
- Place the factors of
into the first position of each set of parentheses:
- The third term of the trinomial is 6. We seek two numbers whose
(a) product is 6 and
(b) sum is 5.
The required numbers are 3 and 2. Place
into the parentheses.
The factorization is complete. We’ll check to be sure.
- Write two sets of parentheses:
.
- Place the factors of
into the first position of each set of parentheses:
- The third term of the trinomial is
. We seek two numbers whose
(a) product is
and
(b) sum is
.
The required numbers are
. Place
into the parentheses.
The factorization is complete. We’ll check to be sure.
Notice that the other combinations of the factors of
(some of which are
) do not work. For example,
In all of these equations, the middle terms are incorrect.
- Write two sets of parentheses:
.
- Place the factors of
into the first position of each set of parentheses:
- The third term of the trinomial is
. We seek two numbers whose
(a) product is 30 and
(b) sum is
.
The required numbers are
. Place
into the parentheses.
The factorization is complete. We’ll check to be sure.
Before we begin, let’s recall the most basic rule of factoring:
factor out common monomial factors first . Notice that 3 is the greatest common monomial factor of
every term. Factor out 3.
Now we can continue.
- Write two sets of parentheses:
.
- Place the factors of
into the first position of each set of parentheses:
- The third term of the trinomial is
. We seek two numbers whose
(a) product is
and
(b) sum is
.
The required numbers are
. Place
into the parentheses.
The factorization is complete. We’ll check to be sure.
Practice set a
Factor, if possible, the following trinomials.
Factoring hints
Factoring trinomials may take some practice, but with time and experience, you will be able to factor much more quickly.
There are some clues that are helpful in determining the factors of the third term that when added yield the coefficient of the middle term.
Factoring hints
Look at the
sign of the last term
:
- If the sign is positive, we know that the two factors must have the
same sign, since
. The two factors will have the same sign as the sign of the middle term.
- If the sign is negative, we know that two factors must have
opposite signs, since
.
Sample set b
Factor
.
- Write two sets of parentheses:
.
- The third term of the trinomial is
. The sign is positive, so the two factors of 12 we are looking for must have the same sign. They will have the sign of the middle term. The sign of the middle term is negative, so both factors of 12 are negative. They are
. Only the factors
are the proper factors of 12 to be used.
Practice set b
Factor, if possible, the following trinomials.
Exercises
For the following problems, factor the trinomials when possible.
(
Hint: Always search for a common factor.)
Exercises for review
(
[link] ) Factor
.
(
[link] ) Factor
.