| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before looking at this module, hopefully you have an idea of what a signal is and what basic classifications and properties a signal canhave. In review, a signal is a function defined with respect to an independent variable. This variable is often timebut could represent any number of things. Mathematically, discrete time analogsignals have discrete independent variables and continuous dependent variables. This module will describe some useful discrete time analog signals.
One of the most important elemental signal that you will deal with is the real-valued sinusoid. In its discrete-timeform, we write the general expression as
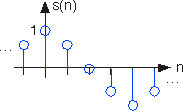
As important as the general sinusoid, the complex exponential function will become a critical part of your study of signals and systems. Its general discrete form iswritten as
The discrete time complex exponentials have the following property.
The second-most important discrete-time signal is the unit sample , which is defined as
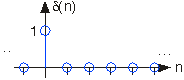
More detail is provided in the section on the discrete time impulse function. For now, it suffices to say that this signal is crucially important in the study of discrete signals, as it allows the sifting property to be used in signal representation and signal decomposition.
Another very basic signal is the unit-step function defined as
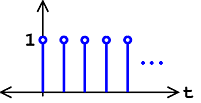

The step function is a useful tool for testing and for defining other signals. For example, whendifferent shifted versions of the step function are multiplied by other signals, one can select a certain portion of thesignal and zero out the rest.
Some of the most important and most frequently encountered signals have been discussed in this module. There are, of course, many other signals of significant consequence not discussed here. As you will see later, many of the other more complicated signals will be studied in terms of those listed here. Especially take note of the complex exponentials and unit impulse functions, which will be the key focus of several topics included in this course.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?