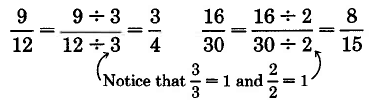This module is from Fundamentals of Mathematics by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr. This module discusses equivalent fractions, reducing fractions to lowest terms, and raising fractions to higher terms. By the end of the module students should be able to recognize equivalent fractions, reduce a fraction to lowest terms and be able to raise a fraction to higher terms.
Section overview
- Equivalent Fractions
- Reducing Fractions to Lowest Terms
- Raising Fractions to Higher Terms
Equivalent fractions
Let's examine the following two diagrams.
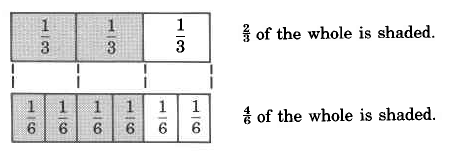
Notice that both
and
represent the
same part of the whole, that is, they represent the same number.
Equivalent fractions
Fractions that have the same value are called
equivalent fractions . Equivalent fractions may look different, but they are still the same point on the number line.
There is an interesting property that equivalent fractions satisfy.
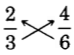
A test for equivalent fractions using the cross product
These pairs of products are called
cross products .
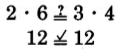
If the cross products are equal, the fractions are equivalent. If the cross products are not equal, the fractions are not equivalent.
Thus,
and
are equivalent, that is,
.
Sample set a
Determine if the following pairs of fractions are equivalent.
. Test for equality of the cross products.
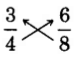
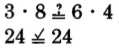 The cross products are equals.
The cross products are equals.
The fractions
and
are equivalent, so
.
. Test for equality of the cross products.
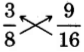
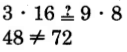 The cross products are
not equal.
The cross products are
not equal.
The fractions
and
are not equivalent.
Practice set a
Determine if the pairs of fractions are equivalent.
,
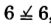 , yes
, yes
,
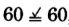 , yes
, yes
,
,
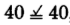 , yes
, yes
,
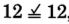 , yes
, yes
Reducing fractions to lowest terms
It is often very useful to
conver t one fraction to an equivalent fraction that has reduced values in the numerator and denominator. We can suggest a method for doing so by considering the equivalent fractions
and
. First, divide both the numerator and denominator of
by 3. The fractions
and
are equivalent.
(Can you prove this?) So,
. We wish to convert
to
. Now divide the numerator and denominator of
by 3, and see what happens.
The fraction
is converted to
.
A natural question is "Why did we choose to divide by 3?" Notice that
We can see that the
factor 3 is common to both the numerator and denominator.
Reducing a fraction
From these observations we can suggest the following method for converting one fraction to an equivalent fraction that has reduced values in the numerator and denominator. The method is called
reducing a fraction .
A fraction can be
reduced by dividing
both the numerator and denominator by the
same nonzero whole number.
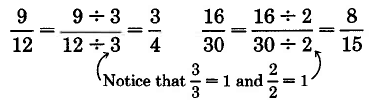
Consider the collection of equivalent fractions
,
,
,
,
Reduced to lowest terms
Notice that each of the first four fractions can be
reduced to the last fraction,
, by dividing both the numerator and denominator by, respectively, 5, 4, 3, and 2. When a fraction is converted to the fraction that has the smallest numerator and denominator in its collection of equivalent fractions, it is said to be
reduced to lowest terms . The fractions
,
,
, and
are all reduced to lowest terms.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() The cross products are equals.
The cross products are equals.![]()
![]() The cross products are
not equal.
The cross products are
not equal.![]() , yes
, yes![]() , yes
, yes![]() , yes
, yes![]() , yes
, yes