| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
(From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia)
Hash algorithms are designed to be fast and to yield few hash collisions in expected input domains. In hash tables and data processing , collisions inhibit the distinguishing of data, making records more costly to find.
A hash algorithm must be deterministic , i.e. if two hashes generated by some hash function are different, then the two inputs were different in some way.
Hash algorithms are usually not injective , i.e. the computed hash value may be the same for different input values. This is because it is usually a requirement that the hash value can be stored in fewer bits than the data being hashed. It is a design goal of hash functions to minimize the likelihood of such a hash collision occurring.
A desirable property of a hash function is the mixing property: a small change in the input (e.g. one bit) should cause a large change in the output (e.g. about half of the bits). This is called the avalanche effect .
Typical hash functions have an infinite domain , such as byte strings of arbitrary length, and a finite range, such as bit sequences of some fixed length. In certain cases, hash functions can be designed with one-to-one mapping between identically sized domain and range. Hash functions that are one-to-one are also called permutations . Reversibility is achieved by using a series of reversible "mixing" operations on the function input.
(From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia)
In computer science, a hash list is typically a list of hashes of the data blocks in a file or set of files. Lists of hashes are used for many different purposes, such as fast table lookup (hash tables) and distributed databases (distributed hash tables). This article covers hash lists that are used to guarantee data integrity.
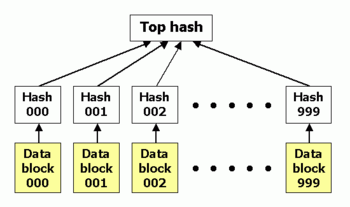
A hash list is an extension of the old concept of hashing an item (for instance, a file). A hash list is usually sufficient for most needs, but a more advanced form of the concept is a hash tree.
Hash lists can be used to protect any kind of data stored, handled and transferred in and between computers. Currently the main use of hash lists is to make sure that data blocks received from other peers in a peer-to-peer network are received undamaged and unaltered, and to check that the other peers do not "lie" and send fake blocks.
Usually a cryptographic hash function such as SHA-1 is used for the hashing. If the hash list only needs to protect against unintentional damage less secure checksums such as CRCs can be used.
Hash lists are better than a simple hash of the entire file since, in the case of a data block being damaged, this is noticed, and only the damaged block needs to be redownloaded. With only a hash of the file, the whole file would have to be redownloaded instead, since it would be impossible to determine which part of the file was damaged. Hash lists also protect against nodes that try to sabotage by sending fake blocks, since in such a case the damaged block can be acquired from some other source.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Data structures and algorithms' conversation and receive update notifications?