This module is published by NCPEA Press and is presented as an NCPEA/Connexions publication. Each chapter has been peer-reviewed, accepted, and endorsed by the National Council of Professors of Educational Administration (NCPEA) as a significant contribution to the scholarship and practice of education administration. Formatted and edited in Connexions by Theodore Creighton and Brad Bizzell, Virginia Tech and Janet Tareilo, Stephen F. Austin State University.
Writing up your nonparametric independent samples t
About the Authors
-
John R. Slate is a Professor at Sam Houston State University where he teaches Basic and Advanced Statistics courses, as well as professional writing, to doctoral students in Educational Leadership and Counseling. His research interests lie in the use of educational databases, both state and national, to reform school practices. To date, he has chaired and/or served over 100 doctoral student dissertation committees. Recently, Dr. Slate created a website,
Writing and Statistical Help to assist students and faculty with both statistical assistance and in editing/writing their dissertations/theses and manuscripts.
-
Ana Rojas-LeBouef is a Literacy Specialist at the Reading Center at Sam Houston State University where she teaches developmental reading courses. She recently completed her doctoral degree in Reading, where she conducted a 16-year analysis of Texas statewide data regarding the achievement gap. Her research interests lie in examining the inequities in achievement among ethnic groups. Dr. Rojas-LeBouef also assists students and faculty in their writing and statistical needs on the Writing and Statistical website,
Writing and Statistical Help
The following is an example of how to write up (in manuscript text) your Nonparametric Independent Samples
t test statistics. This module is used with a larger Collection (Book) authored by John R. Slate and Ana Rojas-LeBouef from Sam Houston State University and available at:
Calculating Basic Statistical Procedures in SPSS: A Self-Help and Practical Guide to Preparing Theses, Dissertations, and Manuscripts
Gender Differences in Arithmetic Among Grade 4 Students
Research question
In this study the following research question was addressed:
- What is the effect of gender on Arithmetic scores among Grade 4 students?
Results
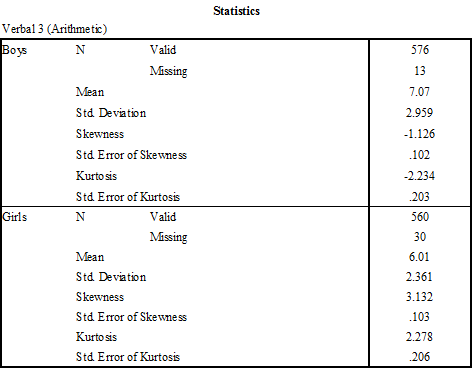
An examination of the standardized skewness coefficient (i.e., the skewness value divided by the standard error of the skewness) and standardized kurtosis coefficient (i.e., the kurtosis value divided by the standard error of the kurtosis) revealed serious departures from normality for the dependent variable, Arithmetic, for both boys and girls. Depicted in Table 1 are the four standardized coefficients, all of which were far beyond the boundaries of normality, +/- 3 (Onwuegbuzie&Daniel, 2002).
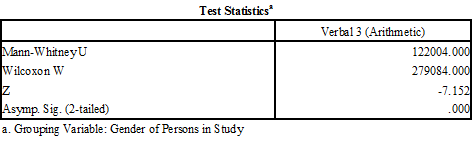
Because Arithmetic scores for boys and for girls were not normally distributed, a nonparametric (i.e., Mann-Whitney’s
U ) independent samples
t -test was used to compare the Arithmetic scores of boys and girls. The Mann-Whitney
U test revealed a statistically significant gender difference in Arithmetic scores,
U = 122004.00,
p <.001. The Cohen’s
d effect size associated with this difference was 0.40. Using Cohen’s (1988) criteria, this finding represented a small-to-moderate effect size. Presented in Table 2 are the descriptive statistics for Arithmetic scores for boys and for girls. Boys had statistically significantly higher Arithmetic scores than did girls.
References
- Cohen, J. (1988).
Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.)
. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Onwuegbuzie, A. J.,&Daniel, L. G. (2002). Uses and misuses of the correlation coefficient.
Research in the Schools, 9 (1)
, 73-90.
To be compliant with APA 6th edition, students and faculty are to be aware that Table titles are placed "above" the table entry. Titles here are placed below the tables because of special formatting templates and for conciseness of visual presentation.
Standardized Skewness Coefficients and Standardized Kurtosis Coefficients for Arithmetic Scores by Gender
| Variable |
Standardized Skewness Coefficient |
Standardized Kurtosis Coefficient |
| Boys |
-11.04 |
-11.00 |
| Girls |
30.41 |
11.06 |
Sample Sizes, Means, and Standard Deviations by Gender for Arithmetic Scores
| Gender |
n |
M |
SD |
| Boys |
576 |
7.07 |
2.96 |
| Girls |
560 |
6.01 |
2.36 |
Figures 1 and 2 below came directly from SPSS output. As such, they are not compliant with APA
6th edition and should not be used in theses, dissertations, or manuscripts. Only Table 1 and 2above the Output from SPSS are compliant with APA format.
Spss statistical output