| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
There are several different types of RNA, each having different functions in the cell. The structure of RNA is similar to DNA with a few small exceptions. For one thing, unlike DNA, most types of RNA, including mRNA, are single-stranded and contain no complementary strand. Second, the ribose sugar in RNA contains an additional oxygen atom compared with DNA. Finally, instead of the base thymine, RNA contains the base uracil. This means that adenine will always pair up with uracil during the protein synthesis process.
Gene expression begins with the process called transcription , which is the synthesis of a strand of mRNA that is complementary to the gene of interest. This process is called transcription because the mRNA is like a transcript, or copy, of the gene’s DNA code. Transcription begins in a fashion somewhat like DNA replication, in that a region of DNA unwinds and the two strands separate, however, only that small portion of the DNA will be split apart. The triplets within the gene on this section of the DNA molecule are used as the template to transcribe the complementary strand of RNA ( [link] ). A codon is a three-base sequence of mRNA, so-called because they directly encode amino acids. Like DNA replication, there are three stages to transcription: initiation, elongation, and termination.
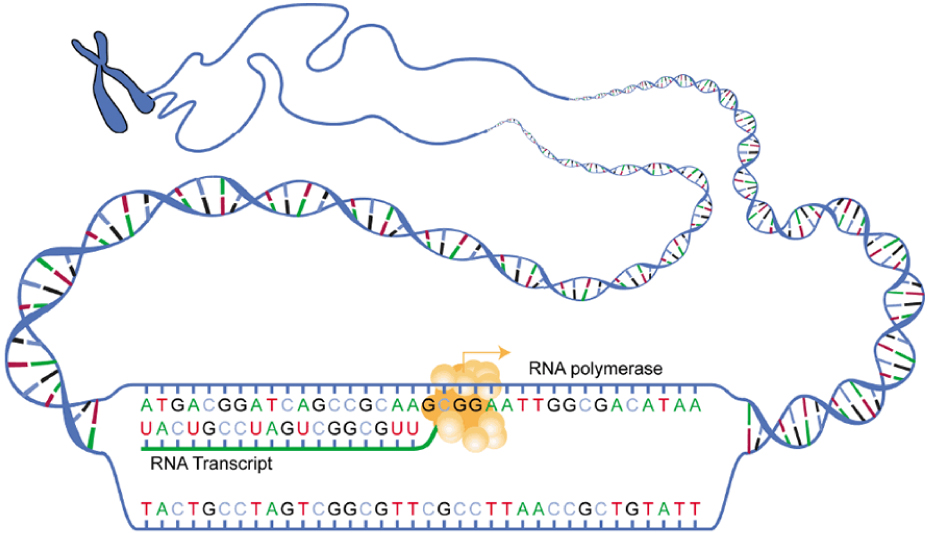
Stage 1: Initiation. A region at the beginning of the gene called a promoter —a particular sequence of nucleotides—triggers the start of transcription.
Stage 2: Elongation. Transcription starts when RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA segment. One strand, referred to as the coding strand, becomes the template with the genes to be coded. The polymerase then aligns the correct nucleic acid (A, C, G, or U) with its complementary base on the coding strand of DNA. RNA polymerase is an enzyme that adds new nucleotides to a growing strand of RNA. This process builds a strand of mRNA.
Stage 3: Termination. When the polymerase has reached the end of the gene, one of three specific triplets (UAA, UAG, or UGA) codes a “stop” signal, which triggers the enzymes to terminate transcription and release the mRNA transcript.
Before the mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus and proceeds to protein synthesis, it is modified in a number of ways. For this reason, it is often called a pre-mRNA at this stage. For example, your DNA, and thus complementary mRNA, contains long regions called non-coding regions that do not code for amino acids. Their function is still a mystery, but the process called splicing removes these non-coding regions from the pre-mRNA transcript ( [link] ). A spliceosome —a structure composed of various proteins and other molecules—attaches to the mRNA and “splices” or cuts out the non-coding regions. The removed segment of the transcript is called an intron . The remaining exons are pasted together. An exon is a segment of RNA that remains after splicing. Interestingly, some introns that are removed from mRNA are not always non-coding. When different coding regions of mRNA are spliced out, different variations of the protein will eventually result, with differences in structure and function. This process results in a much larger variety of possible proteins and protein functions. When the mRNA transcript is ready, it travels out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ucd bis2a intro to biology v1.2' conversation and receive update notifications?