| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Focus detection
Focus Detection:
One important aspect of images is focus. While qualitatively deciding whether an image is in focus or not is relatively easy, quantitatively it can be quite difficult. One way to detect whether or not an image is in focus is by examining its power spectrum.
It is generally assumed that natural images are made up of fractals, and it can be shown that the power spectrum (power as a function of frequency) of a natural image should fall off as
where f is the frequency.
As an image goes out of focus, it becomes blurred. That is to say that the edges are less sharp. If an image contains less sharp edges, its power spectrum will contain less high-frequency power. The power spectrum of an out-of-focus image should, therefore, fall off faster than an in-focus image.
So by calculating the power spectrum and examining its linear regression on a loglog plot (log[power] vs log[frequency]), we can get an indicator of focus.
The power specturm is simply the square of the two dimensional Fourier transform:
where the two dimensional Fourier transform is given by:
Note that denotes an individual image pixel. You may have noticed that the above equations define a square image. While a non-symmetric two dimensional Fourier transform exists, using square images eases the process.
Because whether or not an image is in focus depends on the magnitude of power as a function of frequency, once the two dimensional power spectrum is computed as above, we radially average the spectrum. That is, the average of the values which lie on a circle a distance R from the origin is taken. Because frequency increases linearly in all directions from the origin, radially averaging the power spectrum gives the average power at one frequency , effectively collapsing the two dimensional spectrum to one dimension. It should be noted that has been centered around baseband, meaning the frequency of the rotionally averaged power spectrum extends from 0 to N/2 -1.
The power spectrum’s falloff on a loglog plot can now be examined to determine focus.
The following images show the results of a linear regression of the power spectrum on a loglog plot for an in-focus image and an out-of-focus image.
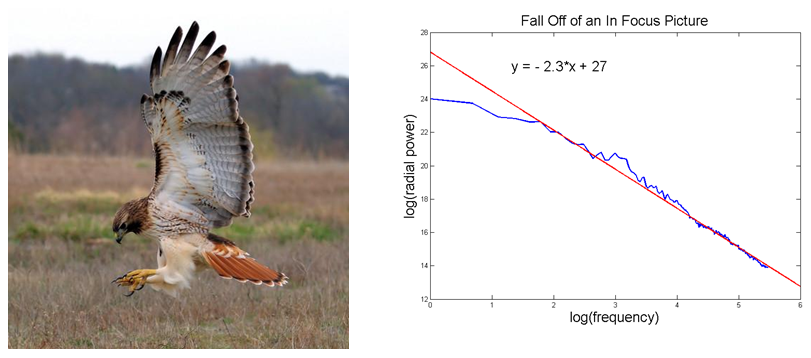
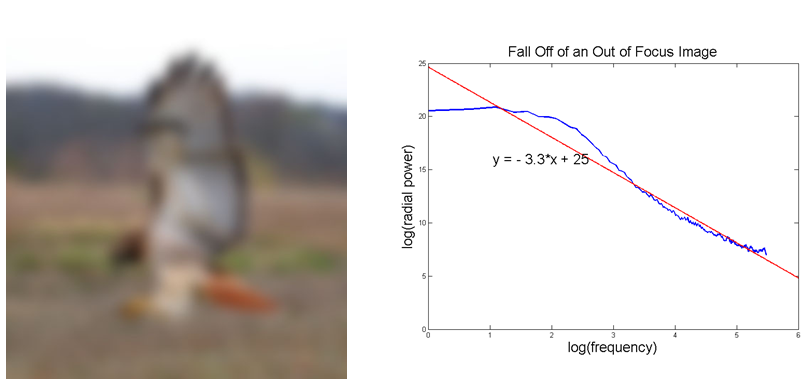
As expected, the out-of-focus image yielded a linear regression with a slope of -3.3, while the in-focus image yielded a linear regression with a slope of -2.3, indicating that the out-of-focus image has fewer high frequency components.
Because frequency and power should be related exponentially as stated before, the loglog plot should display a linear relationship. Taking the linear regression of the loglog plot leads to an estimate of the frequency fall off. For example, if the linear regression where to return a slope of -2, we know that the power spectrum falls off as .
The same principles used to determine whether or not an image is in focus can be used to determine what region of an image is in focus. Because cameras can only focus on one spatial plane, in a single picture certain objects will be more in focus than others. To determine which region of an image is in focus, one simply has to divide the image into separate spatial region and then use the methods described above on each region. The region whose power spectrum conforms most closely to the fall off can be considered the center of focus in the image.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Adaptive region of interest for video' conversation and receive update notifications?