| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When you look at the matter, or physical substances, around you, you will realise that atoms seldom exist on their own. More often, the things around us are made up of different atoms that have been joined together. This is called chemical bonding . Chemical bonding is one of the most important processes in chemistry because it allows all sorts of different molecules and combinations of atoms to form, which then make up the objects in the complex world around us.
A chemical bond is formed when atoms are held together by attractive forces. This attraction occurs when electrons are shared between atoms, or when electrons are exchanged between the atoms that are involved in the bond. The sharing or exchange of electrons takes place so that the outer energy levels of the atoms involved are filled and the atoms are more stable. If an electron is shared , it means that it will spend its time moving in the electron orbitals around both atoms. If an electron is exchanged it means that it is transferred from one atom to another, in other words one atom gains an electron while the other loses an electron.
The type of bond that is formed depends on the elements that are involved. In this chapter, we will be looking at three types of chemical bonding: covalent , ionic and metallic bonding .
You need to remember that it is the valence electrons that are involved in bonding and that atoms will try to fill their outer energy levels so that they are more stable (or are more like the noble gases which are very stable).
Covalent bonding occurs between the atoms of non-metals . The outermost orbitals of the atoms overlap so that unpaired electrons in each of the bonding atoms can be shared. By overlapping orbitals, the outer energy shells of all the bonding atoms are filled. The shared electrons move in the orbitals around both atoms. As they move, there is an attraction between these negatively charged electrons and the positively charged nuclei, and this force holds the atoms together in a covalent bond.
Below are a few examples. Remember that it is only the valence electrons that are involved in bonding, and so when diagrams are drawn to show what is happening during bonding, it is only these electrons that are shown. Circles and crosses are used to represent electrons in different atoms.
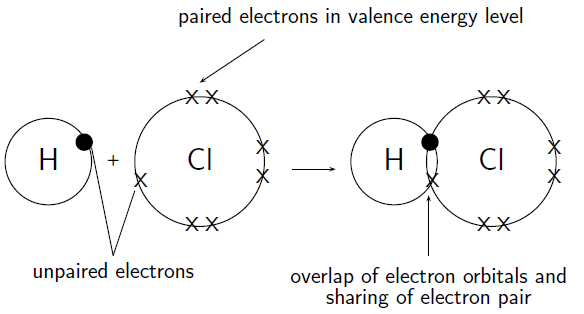
How do hydrogen and chlorine atoms bond covalently in a molecule of hydrogen chloride?
A chlorine atom has 17 electrons, and an electron configuration of . A hydrogen atom has only 1 electron, and an electron configuration of .
Chlorine has 7 valence electrons. One of these electrons is unpaired. Hydrogen has 1 valence electron and it is unpaired.
The hydrogen atom needs one more electron to complete its valence shell. The chlorine atom also needs one more electron to complete its shell. Therefore one pair of electrons must be shared between the two atoms. In other words, one electron from the chlorine atom will spend some of its time orbiting the hydrogen atom so that hydrogen's valence shell is full. The hydrogen electron will spend some of its time orbiting the chlorine atom so that chlorine's valence shell is also full. A molecule of hydrogen chloride is formed ( [link] ). Notice the shared electron pair in the overlapping orbitals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry grade 10 [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?