| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
NMF provides an alternative approach to decomposition that assumes that the data and the components are non-negative. The model for continuous data looks like this: There are two views for NMF, and they provide different insights.
PCA tends to group both positively correlated and negatively correlated components together (it’s only looking for variables with strong correlation). On the other hand, NMF, by forcing W and H to be positive, finds patterns with the same direction of correlation.
W is sparse and it gives probabilistic cluster memberships (columns of W corresponds to kth cluster) and columns of H gives variables that define the kth cluster.
For count data, the model looks slightly different (related to Poisson):
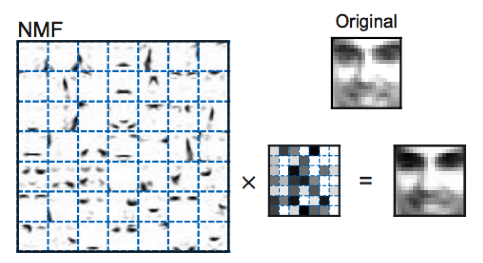
When used on non-negative data such as images, NMF learns a parts-based representation of the dataset, resulting in interpretable models; while PCA learns the holistic representation.Example of facial recognition:
Basis image given by nmf
Basis image given by pca
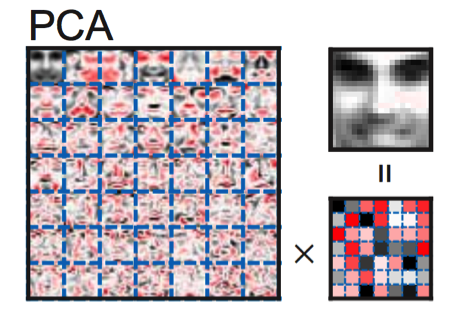
All three algorithms (PCA, ICA and NMF) learn to represent a face using linear combination of basis images. We see that NMF picks out individual components like nose, eyes and mouth, which corresponds well with our intuitive notion of faces. The reason for this is that first, only additive combinations are allowed in NMF and so this is compatible with the intuitive notion of combining parts to form a whole. Second, the basis images are sparse (It is an advantage because they are non-global and should contain several versions of mouths, noses etc. The variability of the face is generated by combining these different parts). PCA, on the other hand, gives out noisy components that doesn’t offer much interpretability. The reason for this is because first, PCA lets each face to be approximated by a linear combination of all the basis images (the vectors aren't sparse) and secondly, it allows the entries of the factorized vectors to be of arbitrary sign. And since these generally involve complex cancellations between positive and negative numbers, many basis images will lack intuitive meaning. ICA basis images (which isn's shown here), are independent holistic representations. The independence assumption made by ICA is ill-suited for learning parts-based representation because various parts are likely to occur together.
This is a biconvex optimization problem (convex in H when W fixed, convex in W when H fixed). For implementation, we used the nnmf command in Matlab (this algorithm uses Alternating Least Squares for solving).
More generally, NMF models the directly observable variables from the hidden variables, where each hidden variable activates a subset of visible variables ("part"). Activation of a collection of hidden variables combine these parts additively to generate a whole. Seen from this perspective, another often used application of NMF is semantic analysis of text document (think text mining).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Comparison of three different matrix factorization techniques for unsupervised machine learning' conversation and receive update notifications?