| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
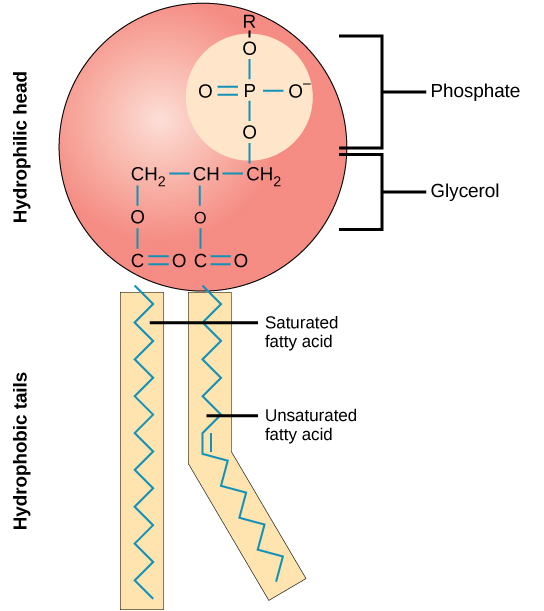
A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule, meaning it has a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic part. The fatty acid chains are hydrophobic and cannot interact with water, whereas the phosphate-containing group is hydrophilic and interacts with water ( [link] ).
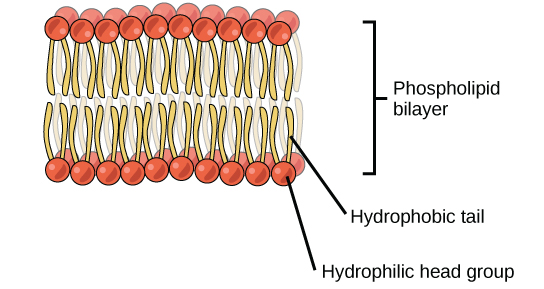
The head is the hydrophilic part, and the tail contains the hydrophobic fatty acids. In a membrane, a bilayer of phospholipids forms the matrix of the structure, the fatty acid tails of phospholipids face inside, away from water, whereas the phosphate group faces the outside, aqueous side ( [link] ).
Phospholipids are responsible for the dynamic nature of the plasma membrane. If a drop of phospholipids is placed in water, it spontaneously forms a structure known as a micelle, where the hydrophilic phosphate heads face the outside and the fatty acids face the interior of this structure.
Unlike the phospholipids and fats discussed earlier, steroids have a fused ring structure. Although they do not resemble the other lipids, they are grouped with them because they are also hydrophobic and insoluble in water. All steroids have four linked carbon rings and several of them, like cholesterol, have a short tail ( [link] ). Many steroids also have the –OH functional group, which puts them in the alcohol classification (sterols).
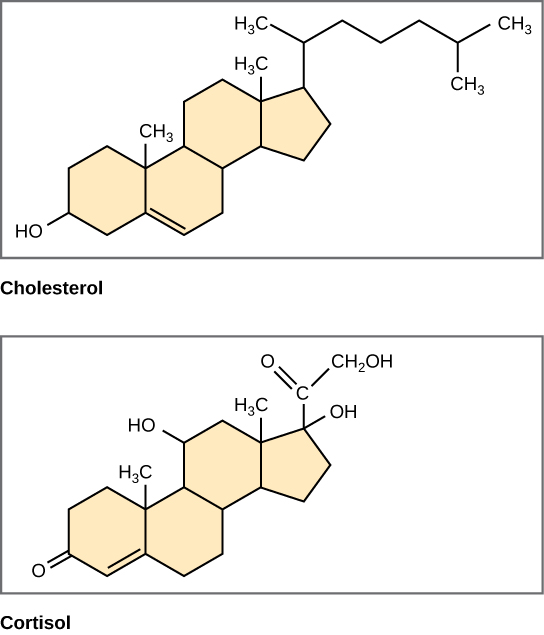
Cholesterol is the most common steroid. Cholesterol is mainly synthesized in the liver and is the precursor to many steroid hormones such as testosterone and estradiol, which are secreted by the gonads and endocrine glands. It is also the precursor to Vitamin D. Cholesterol is also the precursor of bile salts, which help in the emulsification of fats and their subsequent absorption by cells. Although cholesterol is often spoken of in negative terms by lay people, it is necessary for proper functioning of the body. It is a component of the plasma membrane of animal cells and is found within the phospholipid bilayer. Being the outermost structure in animal cells, the plasma membrane is responsible for the transport of materials and cellular recognition and it is involved in cell-to-cell communication.
For an additional perspective on lipids, explore the interactive animation “Biomolecules: The Lipids” . For more information on lipids, please visit the UCD Chemwiki site at Chemwiki lipids
Another perspective on lipids, that contains a variety of animations to help you, is the following link from Carnegie Mellon University, Department of Biological Sciences flash tutorial on lipids .
Which molecule makes up the bulk of a cell's membrane?
f
Which lipid is mainly used for energy storage?
a
Lipids are a class of macromolecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature. Major types include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Fats are a stored form of energy and are also known as triacylglycerols or triglycerides. Fats are made up of fatty acids and either glycerol or sphingosine. Fatty acids may be unsaturated or saturated, depending on the presence or absence of double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain. If only single bonds are present, they are known as saturated fatty acids. Unsaturated fatty acids may have one or more double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain. Phospholipids make up the matrix of membranes. They have a glycerol or sphingosine backbone to which two fatty acid chains and a phosphate-containing group are attached. Steroids are another class of lipids. Their basic structure has four fused carbon rings. Cholesterol is a type of steroid and is an important constituent of the plasma membrane, where it helps to maintain the fluid nature of the membrane. It is also the precursor of steroid hormones such as testosterone.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ucd bis2a intro to biology v1.2' conversation and receive update notifications?