| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Supercritical internal reflection refers to angles of incidence above the critical angle of incidence allowing total internal reflectance. It is in this angular regime where only incident and reflected waves will be present. The transmitted wave is confined to the interface where its amplitude is at a maximum and will damp exponentially into the lower refractive index medium as a function of distance. This wave is referred to as the evanescent wave and it extends only a very short distance beyond the interface.
To apply total internal reflection to the experimental setup in ATR, consider n 2 to be the internal reflectance element or ATR crystal (the blue trapezoid in [link] ) where n 2 is the material with the higher index of refraction. This should be a material that is fully transparent to the incident infrared radiation to give a real value for the refractive index. The ATR crystal must also have a high index of refraction to allow total internal reflection with many samples that have an index of refraction n 1 , where n 1 < n 2 .
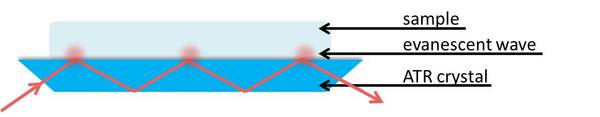
We can consider the sample to be absorbing in the infrared. Electromagnetic energy will pass through the crystal/sample interface and propagate into the sample via the evanescent wave. This energy loss must be compensated with the incident IR light. Thus, total reflectance is no longer occurring and the reflection inside the crystal is attenuated. If a sample does not absorb, the reflectance at the interface shows no attenuation. Therefore if the IR light at a particular frequency does not reach the detector, the sample must have absorbed it.
The penetration depth of the evanescent wave within the sample is on the order of 1µm. The expression of the penetration depth is given in [link] and is dependent upon the wavelength and angle of incident light as well as the refractive indices of the ATR crystal and sample. The effective path length is the product of the depth of penetration of the evanescent wave and the number of points that the IR light reflects at the interface between the crystal and sample. This path length is equivalent to the path length of a sample in a traditional transmission FTIR setup.
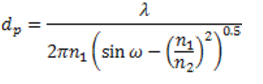
Typically an ATR attachment can be used with a traditional FTIR where the beam of incident IR light enters a horizontally positioned crystal with a high refractive index in the range of 1.5 to 4, as can be seen in [link] . This refractive index should be greater than that of the sample. Generally, samples will consist of organic compounds, inorganic compounds, and polymers which have refractive indices below 2 and can readily be found on a database.
| Material | Refractive index (RI) | Spectral range (cm -1 ) |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc Selenide (ZnSe) | 2.4 | 20000-650 |
| Germanium (Ge) | 4 | 5500-870 |
| Sapphire (Al 2 O 3 ) | 1.74 | 50000-2000 |
| Diamond (C) | 2.4 | 45000-2500 and 1650-200 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?