| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The secondary filter is placed at a 90° angle ( [link] ) to the original light path to minimize the risk of transmitted or reflected incident light reaching the detector. Also this minimizes the amount of stray light, and results in a better signal-to-noise ratio. From the secondary filter, wavelengths specific to the sample are passed onto the detector.
The detector can either be single-channeled or multichanneled ( [link] ). The single-channeled detector can only detect the intensity of one wavelength at a time, while the multichanneled detects the intensity at all wavelengths simultaneously, making the emission monochromator or filter unnecessary. The different types of detectors have both advantages and disadvantages.
The output is the form of a plot of intensity of emitted light as a function of wavelength as shown in [link] .
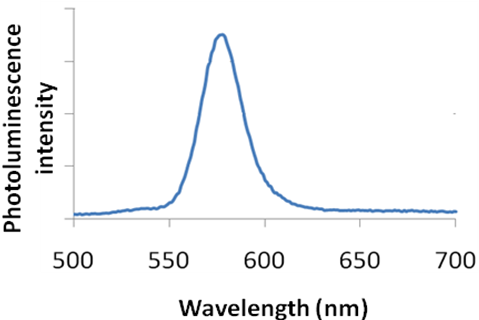
The data obtained from fluorimeter is a plot of fluorescence intensity as a function of wavelength. Quantitative and qualitative data can be obtained by analysing this information.
From the fluorescence intensity versus wavelength data, the quantum yield (Φ F ) of the sample can be determined. Quantum yield is a measure of the ratio of the photons absorbed with respect to the photons emitted. It is important for the application of Group 12-16 semiconductor quantum dots using their fluorescence properties, for e.g., bio-markers.
The most well-known method for recording quantum yield is the comparative method which involves the use of well characterized standard solutions. If a test sample and a standard sample have similar absorbance values at the same excitation wavelength, it can be assumed that the number of photons being absorbed by both the samples is the same. This means that a ratio of the integrated fluorescence intensities of the test and standard sample measured at the same excitation wavelength will give a ratio of quantum yields. Since the quantum yield of the standard solution is known, the quantum yield for the unknown sample can be calculated.
A plot of integrated fluorescence intensity versus absorbance at the excitation wavelength is shown in [link] . The slope of the graphs shown in [link] are proportional to the quantum yield of the different samples. Quantum yield is then calculated using [link] , where subscripts ST denotes standard sample and X denotes the test sample; QY is the quantum yield; RI is the refractive index of the solvent.
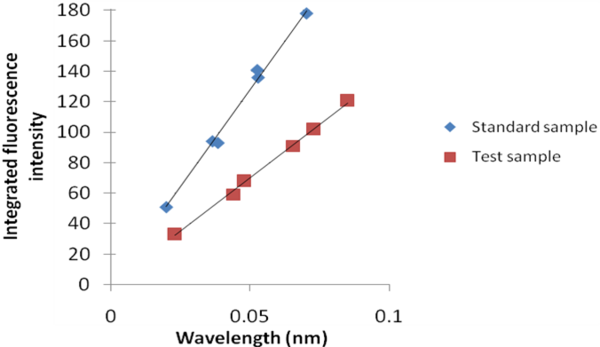
Take the example of [link] . If the same solvent is used in both the sample and the standard solution, the ratio of quantum yields of the sample to the standard is given by [link] . If the quantum yield of the standard is known to 0.95, then the quantum yield of the test sample is 0.523 or 52.3%.
The assumption used in the comparative method is valid only in the Beer-Lambert law linear regime. Beer-Lambert law states that absorbance is directly proportional to the path length of light travelled within the sample, and concentration of the sample. The factors that affect the quantum yield measurements are the following:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?