| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
One of the most sensitive forms of magnetometry is SQUID magnetometry. This uses technique uses a combination of superconducting materials and Josephson junctions to measure magnetic fields with resolutions up to ~10 -14 kG or greater. In the proceeding pages we will describe how a SQUID actually works.
In superconductors the resistanceless current is carried by pairs of electrons, known as Cooper Pairs. A Cooper Pair is a pair of electrons. Each electron has a quantized wavelength. With a Cooper pair each electrons wave couples with its opposite number over a large distances. This phenomenon is a result of the very low temperatures at which many materials will superconduct.
What exactly is superconductance? When a material is at very low temperatures, its crystal lattice behaves differently than when it higher temperatures. Usually at higher temperatures a material will have large vibrations called in the crystal lattice. These vibrations scatter electrons as they pass through this lattice ( [link] ), and this is the basis for bad conductance.
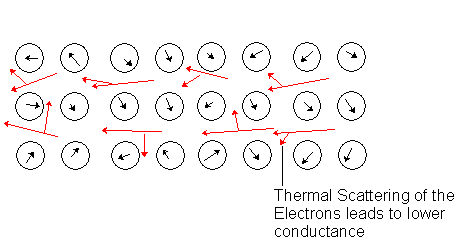
With a superconductor the material is designed to have very small vibrations, these vibrations are lessened even more by cooling the material to extremely low temperatures. With no vibrations there is no scattering of the electrons and this allows the material to superconduct.
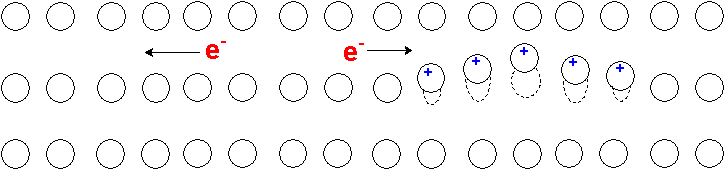
The origin of a Cooper pair is that as the electron passes through a crystal lattice at superconducting temperatures it negative charge pulls on the positive charge of the nuclei in the lattice through coulombic interactions producing a ripple. An electron traveling in the opposite direction is attracted by this ripple. This is the origin of the coupling in a Cooper pair ( [link] ).
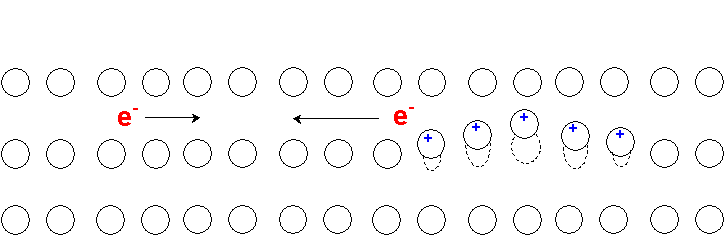
A passing electron attracts the lattice, causing a slight ripple toward its path. Another electron passing in the opposite direction is attracted to that displacement ( [link] ).
Due to the coupling and the fact that for each pair there is two spin states ( [link] ).
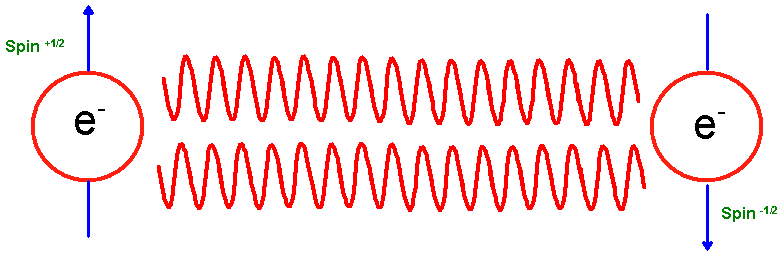
Each pair can be treated as a single particle with a whole spin, not half a spin such as is usually the case with electrons. This is important, as an electron which is classed in a group of matter called Fermions are governed by the Fermi exclusion principle which states that anything with a spin of one half cannot occupy the same space as something with the same spin of one half. This turns the electron means that a Cooper pair is in fact a Boson the opposite of a Fermion and this allows the Coopers pairs to condensate into one wave packet. Each Coopers pair has a mass and charge twice that of a single electron, whose velocity is that of the center of mass of the pair. This coupling can only happen in extremely cold conditions as thermal vibrations become greater than the force that an electron can exert on a lattice. And thus scattering occurs.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?