| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Usually the electron relaxes to the ground state through a combination of both radiative and non-radiative decays. The electron moves quickly through the conduction energy levels through small non-radiative decays and the final transition across the band gap is via a radiative decay. Large nonradiative decays don’t occur across the band gap because the crystal structure can’t withstand large vibrations without breaking the bonds of the crystal. Since some of the energy is lost through the non-radiative decay, the energy of the emitted photon, through the radiative decay, is much lesser than the absorbed energy. As a result the wavelength of the emitted photon or fluorescence is longer than the wavelength of absorbed light. This energy difference is called the Stokes shift. Due this Stokes shift, the emission peak corresponding to the absorption band edge peak is shifted towards a higher wavelength (lower energy), i.e., [link] .
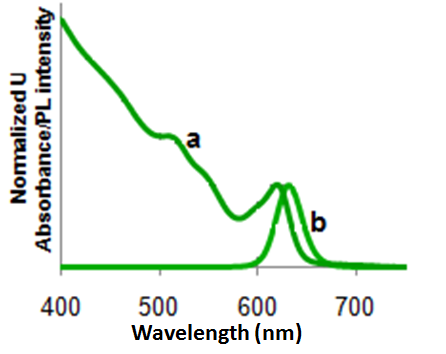
Intensity of emission versus wavelength is a bell-shaped Gaussian curve. As long as the excitation wavelength is shorter than the absorption onset, the maximum emission wavelength is independent of the excitation wavelength. [link] shows a combined absorption and emission spectrum for a typical CdSe tetrapod.
There are various factors that affect the absorption and emission spectra for Group 12-16 semiconductor quantum crystals. Fluorescence is much more sensitive to the background, environment, presence of traps and the surface of the QDs than UV-visible absorption. Some of the major factors influencing the optical properties of quantum nanoparticles include:
The size dependent optical properties of NP’s have many applications from biomedical applications to solar cell technology, from photocatalysis to chemical sensing. Most of these applications use the following unique properties.
For applications in the field of nanoelectronics, the sizes of the quantum dots can be tuned to be comparable to the scattering lengths, reducing the scattering rate and hence, the signal to noise ratio. For Group 12-16 QDs to be used in the field of solar cells, the bandgap of the particles can be tuned so as to form absorb energy over a large range of the solar spectrum, resulting in more number of excitons and hence more electricity. Since the nanoparticles are so small, most of the atoms are on the surface. Thus, the surface to volume ratio is very large for the quantum dots. In addition to a high surface to volume ratio, the Group 12-16 QDs respond to light energy. Thus quantum dots have very good photocatalytic properties. Quantum dots show fluorescence properties, and emit visible light when excited. This property can be used for applications as biomarkers. These quantum dots can be tagged to drugs to monitor the path of the drugs. Specially shaped Group 12-16 nanoparticles such as hollow shells can be used as drug delivery agents. Another use for the fluorescence properties of Group 12-16 semiconductor QDs is in color-changing paints, which can change colors according to the light source used.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?