| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Group 12-16 semiconductor nanocrystals when exposed to light of a particular energy absorb light to excite electrons from the ground state to the excited state, resulting in the formation of an electron-hole pair (also known as excitons). The excited electrons relax back to the ground state, mainly through radiative emission of energy in the form of photons.
Quantum dots (QD) refer to nanocrystals of semiconductor materials where the size of the particles is comparable to the natural characteristic separation of an electron-hole pair, otherwise known as the exciton Bohr radius of the material. In quantum dots, the phenomenon of emission of photons associated with the transition of electrons from the excited state to the ground state is called fluorescence.
Emission spectroscopy, in general, refers to a characterization technique that measures the emission of radiation by a material that has been excited. Fluorescence spectroscopy is one type of emission spectroscopy which records the intensity of light radiated from the material as a function of wavelength. It is a nondestructive characterization technique.
After an electron is excited from the ground state, it needs to relax back to the ground state. This relaxation or loss of energy to return to the ground state, can be achieved by a combination of non-radiative decay (loss of energy through heat) and radiative decay (loss of energy through light). Non-radiative decay by vibrational modes typically occurs between energy levels that are close to each other. Radiative decay by the emission of light occurs when the energy levels are far apart like in the case of the band gap. This is because loss of energy through vibrational modes across the band gap can result in breaking the bonds of the crystal. This phenomenon is shown in [link] .
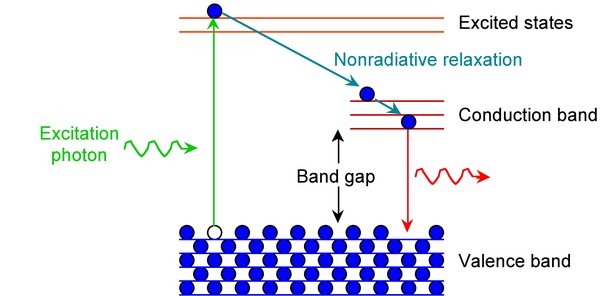
The band gap of Group 12-16 semiconductors is in the UV-visible region. Thus, the wavelength of the emitted light as a result of radiative decay is also in the visible region, resulting in fascinating fluorescence properties.
A fluorimeter is a device that records the fluorescence intensity as a function of wavelength. The fluorescence quantum yield can then be calculated by the ratio of photons absorbed to photons emitted by the system. The quantum yield gives the probability of the excited state getting relaxed via fluorescence rather than by any other non-radiative decay.
Photoluminescence is the emission of light from any material due to the loss of energy from excited state to ground state. There are two main types of luminescence – fluorescence and phosphorescence. Fluorescence is a fast decay process, where the emission rate is around 10 8 s -1 and the lifetime is around 10 -9 - 10 -7 s. Fluorescence occurs when the excited state electron has an opposite spin compared to the ground state electrons. From the laws of quantum mechanics, this is an allowed transition, and occurs rapidly by emission of a photon. Fluorescence disappears as soon as the exciting light source is removed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?