| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price in much the same way as a monopolist. A monopolistic competitor, like a monopolist, faces a downward-sloping demand curve, and so it will choose some combination of price and quantity along its perceived demand curve.
As an example of a profit-maximizing monopolistic competitor, consider the Authentic Chinese Pizza store, which serves pizza with cheese, sweet and sour sauce, and your choice of vegetables and meats. Although Authentic Chinese Pizza must compete against other pizza businesses and restaurants, it has a differentiated product. The firm’s perceived demand curve is downward sloping, as shown in [link] and the first two columns of [link] .
| Quantity | Price | Total Revenue | Marginal Revenue | Total Cost | Marginal Cost | Average Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | $23 | $230 | - | $340 | - | $34 |
| 20 | $20 | $400 | $17 | $400 | $6 | $20 |
| 30 | $18 | $540 | $14 | $480 | $8 | $16 |
| 40 | $16 | $640 | $10 | $580 | $10 | $14.50 |
| 50 | $14 | $700 | $6 | $700 | $12 | $14 |
| 60 | $12 | $720 | $2 | $840 | $14 | $14 |
| 70 | $10 | $700 | –$2 | $1,020 | $18 | $14.57 |
| 80 | $8 | $640 | –$6 | $1,280 | $26 | $16 |
The combinations of price and quantity at each point on the demand curve can be multiplied to calculate the total revenue that the firm would receive, which is shown in the third column of [link] . The fourth column, marginal revenue, is calculated as the change in total revenue divided by the change in quantity. The final columns of [link] show total cost, marginal cost, and average cost. As always, marginal cost is calculated by dividing the change in total cost by the change in quantity, while average cost is calculated by dividing total cost by quantity. The following Work It Out feature shows how these firms calculate how much of its product to supply at what price.
The process by which a monopolistic competitor chooses its profit-maximizing quantity and price resembles closely how a monopoly makes these decisions process. First, the firm selects the profit-maximizing quantity to produce. Then the firm decides what price to charge for that quantity.
Step 1. The monopolistic competitor determines its profit-maximizing level of output. In this case, the Authentic Chinese Pizza company will determine the profit-maximizing quantity to produce by considering its marginal revenues and marginal costs. Two scenarios are possible:
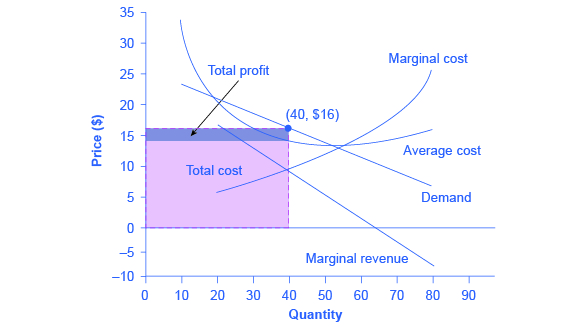
In this example, MR and MC intersect at a quantity of 40, which is the profit-maximizing level of output for the firm.
Step 2. The monopolistic competitor decides what price to charge. When the firm has determined its profit-maximizing quantity of output, it can then look to its perceived demand curve to find out what it can charge for that quantity of output. On the graph, this process can be shown as a vertical line reaching up through the profit-maximizing quantity until it hits the firm’s perceived demand curve. For Authentic Chinese Pizza, it should charge a price of $16 per pizza for a quantity of 40.
Once the firm has chosen price and quantity, it’s in a position to calculate total revenue, total cost, and profit. At a quantity of 40, the price of $16 lies above the average cost curve, so the firm is making economic profits. From [link] we can see that, at an output of 40, the firm’s total revenue is $640 and its total cost is $580, so profits are $60. In [link] , the firm’s total revenues are the rectangle with the quantity of 40 on the horizontal axis and the price of $16 on the vertical axis. The firm’s total costs are the light shaded rectangle with the same quantity of 40 on the horizontal axis but the average cost of $14.50 on the vertical axis. Profits are total revenues minus total costs, which is the shaded area above the average cost curve.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?