| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
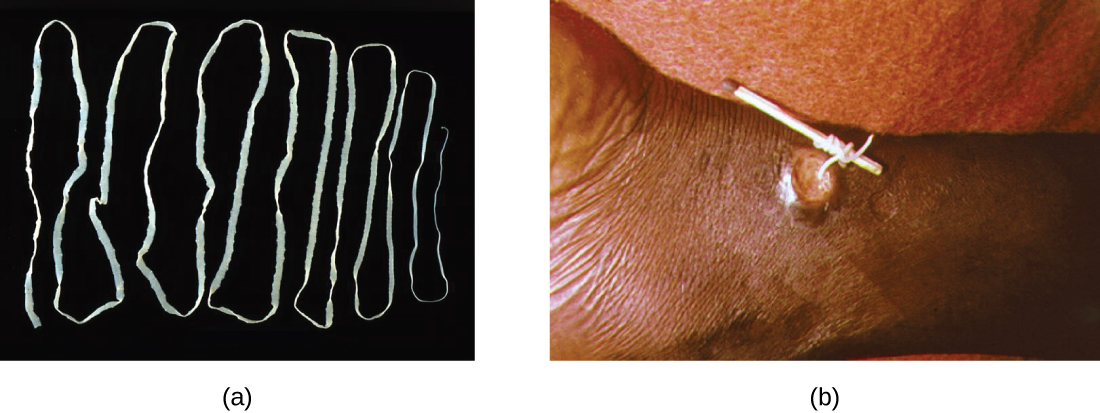
Multicellular parasitic worms called helminth s are not technically microorganisms, as most are large enough to see without a microscope. However, these worms fall within the field of microbiology because diseases caused by helminths involve microscopic eggs and larvae. One example of a helminth is the guinea worm , or Dracunculus medinensis , which causes dizziness, vomiting, diarrhea, and painful ulcers on the legs and feet when the worm works its way out of the skin ( [link] ). Infection typically occurs after a person drinks water containing water fleas infected by guinea-worm larvae. In the mid-1980s, there were an estimated 3.5 million cases of guinea-worm disease, but the disease has been largely eradicated. In 2014, there were only 126 cases reported, thanks to the coordinated efforts of the World Health Organization (WHO) and other groups committed to improvements in drinking water sanitation. C. Greenaway “Dracunculiasis (Guinea Worm Disease).” Canadian Medical Association Journal 170 no. 4 (2004):495–500. World Health Organization. “Dracunculiasis (Guinea-Worm Disease).” WHO . 2015. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs359/en/. Accessed October 2, 2015.
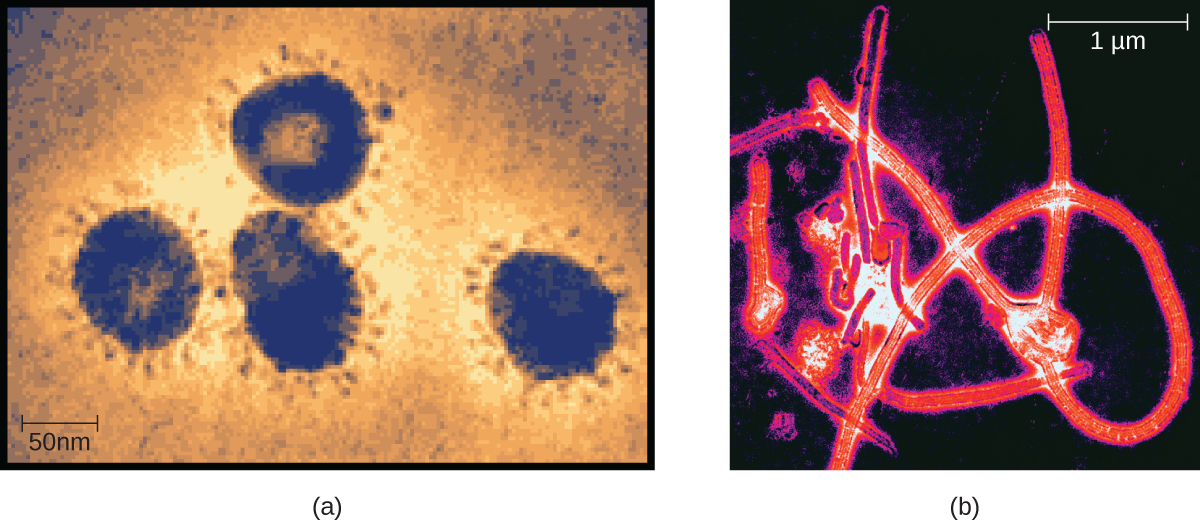
Virus es are acellular microorganisms, which means they are not composed of cells. Essentially, a virus consists of proteins and genetic material—either DNA or RNA, but never both—that are inert outside of a host organism. However, by incorporating themselves into a host cell, viruses are able to co-opt the host’s cellular mechanisms to multiply and infect other hosts.
Viruses can infect all types of cells, from human cells to the cells of other microorganisms. In humans, viruses are responsible for numerous diseases, from the common cold to deadly Ebola ( [link] ). However, many viruses do not cause disease.
Microbiology is a broad term that encompasses the study of all different types of microorganisms. But in practice, microbiologists tend to specialize in one of several subfields. For example, bacteriology is the study of bacteria; mycology is the study of fungi; protozoology is the study of protozoa; parasitology is the study of helminths and other parasites; and virology is the study of viruses ( [link] ). Immunology , the study of the immune system, is often included in the study of microbiology because host–pathogen interactions are central to our understanding of infectious disease processes. Microbiologists can also specialize in certain areas of microbiology, such as clinical microbiology, environmental microbiology, applied microbiology, or food microbiology.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?