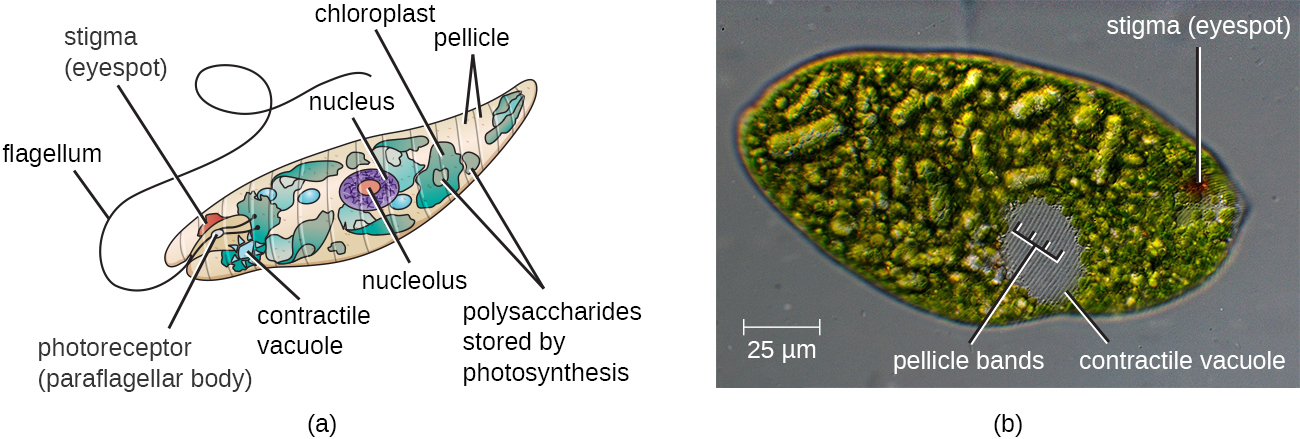
| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The Euglenozoa also include the trypanosomes, which are parasitic pathogens. The genus Trypanosoma includes T. brucei , which causes African trypanosomiasis ( African sleeping sickness and T. cruzi , which causes American trypanosomiasis ( Chagas disease ). These tropical diseases are spread by insect bites. In African sleeping sickness, T. brucei colonizes the blood and the brain after being transmitted via the bite of a tsetse fly ( Glossina spp.) ( [link] ). The early symptoms include confusion, difficulty sleeping, and lack of coordination. Left untreated, it is fatal.
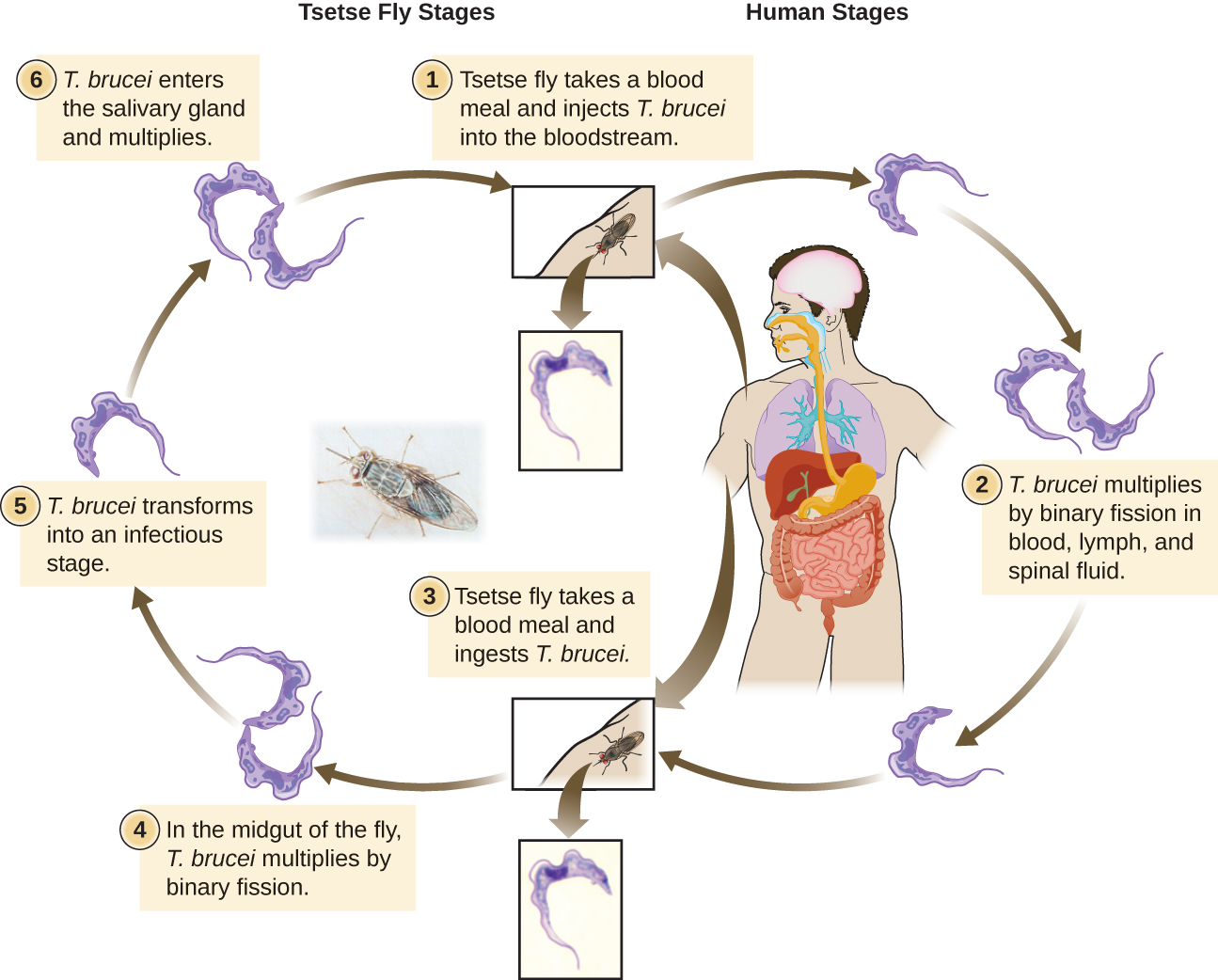
Chagas’ disease originated and is most common in Latin America. The disease is transmitted by Triatoma spp., insects often called “kissing bugs,” and affects either the heart tissue or tissues of the digestive system. Untreated cases can eventually lead to heart failure or significant digestive or neurological disorders.
The genus Leishmania includes trypanosomes that cause disfiguring skin disease and sometimes systemic illness as well.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is responsible for identifying public health priorities in the United States and developing strategies to address areas of concern. As part of this mandate, the CDC has officially identified five parasitic diseases it considers to have been neglected (i.e., not adequately studied). These neglected parasitic infections (NPIs) include toxoplasmosis , Chagas disease , toxocariasis (a nematode infection transmitted primarily by infected dogs), cysticercosis (a disease caused by a tissue infection of the tapeworm Taenia solium ), and trichomoniasis (a sexually transmitted disease caused by the parabasalid Trichomonas vaginalis ).
The decision to name these specific diseases as NPIs means that the CDC will devote resources toward improving awareness and developing better diagnostic testing and treatment through studies of available data. The CDC may also advise on treatment of these diseases and assist in the distribution of medications that might otherwise be difficult to obtain. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Neglected Parasitic Infections (NPIs) in the United States.” http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/npi/. Last updated July 10, 2014.
Of course, the CDC does not have unlimited resources, so by prioritizing these five diseases, it is effectively deprioritizing others. Given that many Americans have never heard of many of these NPIs, it is fair to ask what criteria the CDC used in prioritizing diseases. According to the CDC, the factors considered were the number of people infected, the severity of the illness, and whether the illness can be treated or prevented. Although several of these NPIs may seem to be more common outside the United States, the CDC argues that many cases in the United States likely go undiagnosed and untreated because so little is known about these diseases. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Fact Sheet: Neglected Parasitic Infections in the United States.” http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/resources/pdf/npi_factsheet.pdf
What criteria should be considered when prioritizing diseases for purposes of funding or research? Are those identified by the CDC reasonable? What other factors could be considered? Should government agencies like the CDC have the same criteria as private pharmaceutical research labs? What are the ethical implications of deprioritizing other potentially neglected parasitic diseases such as leishmaniasis?
The plasma membrane of a protist is called the __________.
plasmalemma
Animals belong to the same supergroup as the kingdom __________.
Fungi
What are kinetoplastids?
Aside from a risk of birth defects, what other effect might a toxoplasmosis infection have?
What is the function of the ciliate macronucleus?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?