| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Despite central tolerance, some self-reactive T cells generally escape the thymus and enter the peripheral bloodstream. Therefore, a second line of defense called peripheral tolerance is needed to protect against autoimmune disease. Peripheral tolerance involves mechanisms of anergy and inhibition of self-reactive T cells by regulatory T cells . Anergy refers to a state of nonresponsiveness to antigen stimulation. In the case of self-reactive T cells that escape the thymus, lack of an essential co-stimulatory signal required for activation causes anergy and prevents autoimmune activation. Regulatory T cells participate in peripheral tolerance by inhibiting the activation and function of self-reactive T cells and by secreting anti-inflammatory cytokines.
It is not completely understood what events specifically direct maturation of thymocytes into regulatory T cells. Current theories suggest the critical events may occur during the third step of thymic selection, when most self-reactive T cells are eliminated. Regulatory T cells may receive a unique signal that is below the threshold required to target them for negative selection and apoptosis. Consequently, these cells continue to mature and then exit the thymus, armed to inhibit the activation of self-reactive T cells.
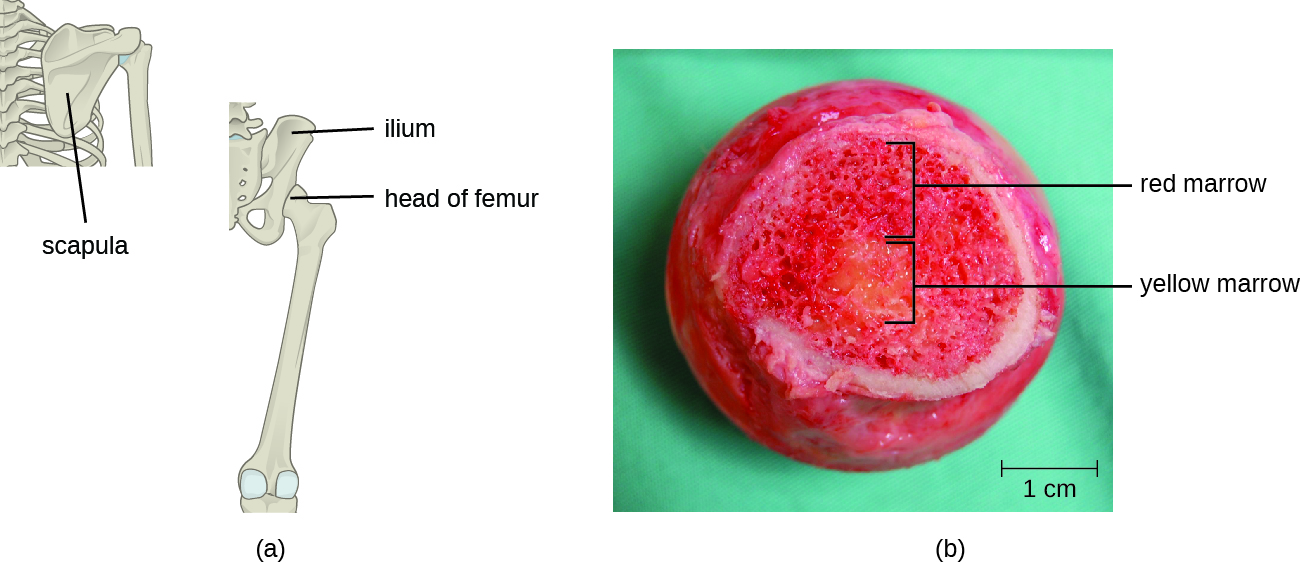
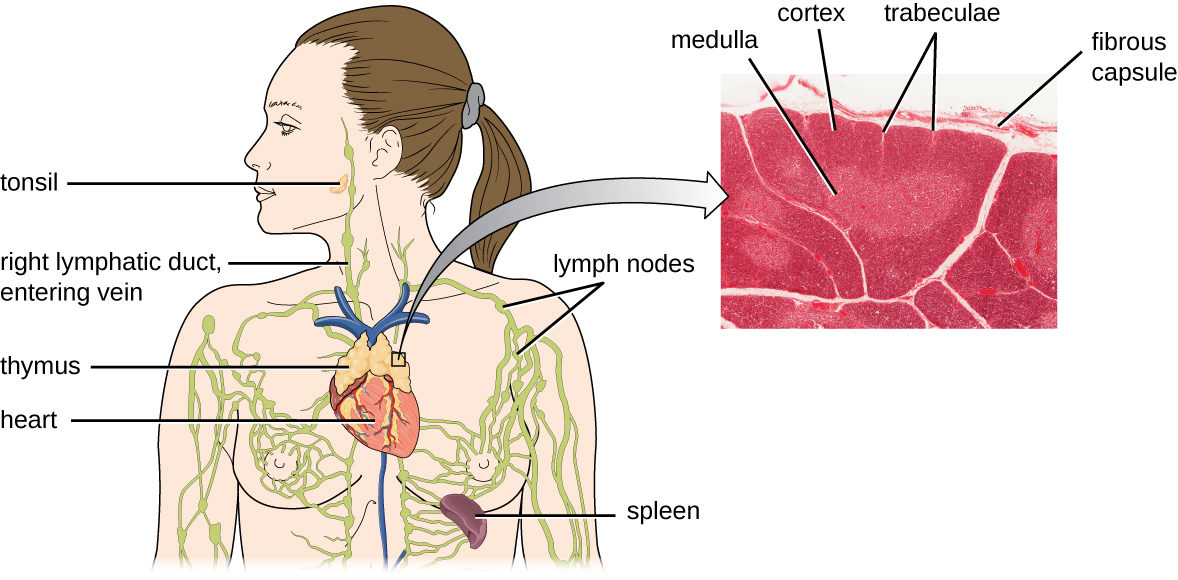
It has been estimated that the three steps of thymic selection eliminate 98% of thymocytes. The remaining 2% that exit the thymus migrate through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to sites of secondary lymphoid organs/tissues, such as the lymph nodes , spleen , and tonsils ( [link] ), where they await activation through the presentation of specific antigens by APCs. Until they are activated, they are known as mature naïve T cells .
T cells can be categorized into three distinct classes: helper T cells , regulatory T cells, and cytotoxic T cells . These classes are differentiated based on their expression of certain surface molecules, their mode of activation, and their functional roles in adaptive immunity ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?