| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Congenital rubella syndrome is the most severe clinical complication of the German measles. This occurs if a woman is infected with rubella during pregnancy . The rubella virus is teratogenic , meaning it can cause developmental defects if it crosses the placenta during pregnancy. There is a very high incidence of stillbirth, spontaneous abortion, or congenital birth defects if the mother is infected before 11 weeks of pregnancy and 35% if she is infected between weeks 13–16; after this time the incidence is low. E. Miller et al. “Consequences of Confirmed Maternal Rubella at Successive Stages of Pregnancy.” The Lancet 320, no. 8302 (1982):781–784. For this reason, prenatal screening for rubella is commonly practiced in the United States. Postnatal infections are usually self-limiting and rarely cause severe complications.
Like measles, the preliminary diagnosis of rubella is based on the patient’s history, vaccination records, and the appearance of the rash. The diagnosis can be confirmed by hemagglutinin inhibition assays and a variety of other immunological techniques. There are no antiviral therapies for rubella, but an effective vaccine ( MMR ) is widely available. Vaccination efforts have essentially eliminated rubella in the United States; fewer than a dozen cases are reported in a typical year.
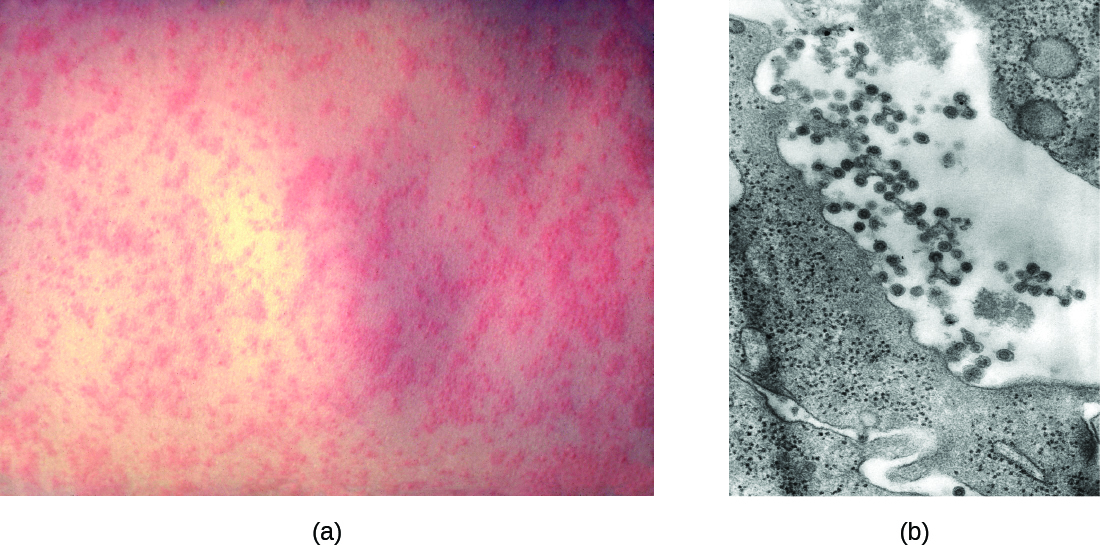
Chickenpox, also known as varicella , was once a common viral childhood disease. The causative agent of chickenpox , the varicella-zoster virus , is a member of the herpesvirus family. In children, the disease is mild and self-limiting, and is easily transmitted by direct contact or inhalation of material from the skin lesions. In adults, however, chickenpox infections can be much more severe and can lead to pneumonia and birth defects in the case of infected pregnant women. Reye syndrome , mentioned earlier in this chapter, is also a serious complication associated with chickenpox, generally in children.
Once infected, most individuals acquire a lifetime immunity to future chickenpox outbreaks. For this reason, parents once held “chickenpox parties” for their children. At these events, uninfected children were intentionally exposed to an infected individual so they would contract the disease earlier in life, when the incidence of complications is very low, rather than risk a more severe infection later.
After the initial viral exposure, chickenpox has an incubation period of about 2 weeks. The initial infection of the respiratory tract leads to viremia and eventually produces fever and chills. A pustular rash then develops on the face, progresses to the trunk, and then the extremities, although most form on the trunk ( [link] ). Eventually, the lesions burst and form a crusty scab. Individuals with chickenpox are infectious from about 2 days before the outbreak of the rash until all the lesions have scabbed over.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?