| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The hydrogen and oxygen atoms within water molecules form polar covalent bonds. There is no overall charge to a water molecule, but there is one ∂ + on each hydrogen atom and two ∂ – on the oxygen atom. Each water molecule attracts other water molecules because of the positive and negative charges in the different parts of the molecule ( [link] ). Water also attracts other polar molecules (such as sugars), forming hydrogen bonds. When a substance readily forms hydrogen bonds with water, it can dissolve in water and is referred to as hydrophilic (“water-loving”). Hydrogen bonds are not readily formed with nonpolar substances like oils and fats. These nonpolar compounds are hydrophobic (“water-fearing”) and will orient away from and avoid water.
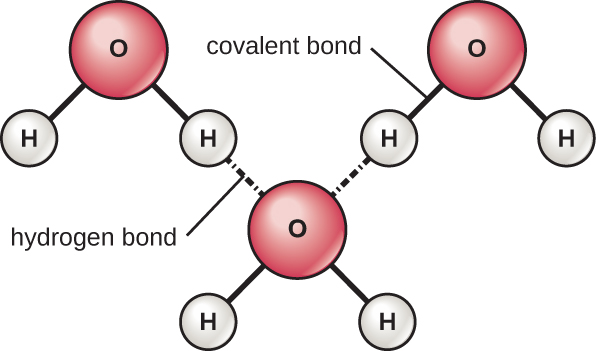
The hydrogen bonds in water allow it to absorb and release heat energy more slowly than many other substances. This means that water moderates temperature changes within organisms and in their environments. As energy input continues, the balance between hydrogen-bond formation and breaking swings toward fewer hydrogen bonds: more bonds are broken than are formed. This process results in the release of individual water molecules at the surface of the liquid (such as a body of water, the leaves of a plant, or the skin of an organism) in a process called evaporation .
Conversely, as molecular motion decreases and temperatures drop, less energy is present to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules. These bonds remain intact and begin to form a rigid, lattice-like structure (e.g., ice). When frozen, ice is less dense (the molecules are farther apart) than liquid water. This means that ice floats on the surface of a body of water. In lakes, ponds, and oceans, ice will form on the surface of the water, creating an insulating barrier to protect the animal and plant life beneath from freezing in the water. If this did not happen, plants and animals living in water would freeze in a block of ice and could not move freely, making life in cold temperatures difficult or impossible.
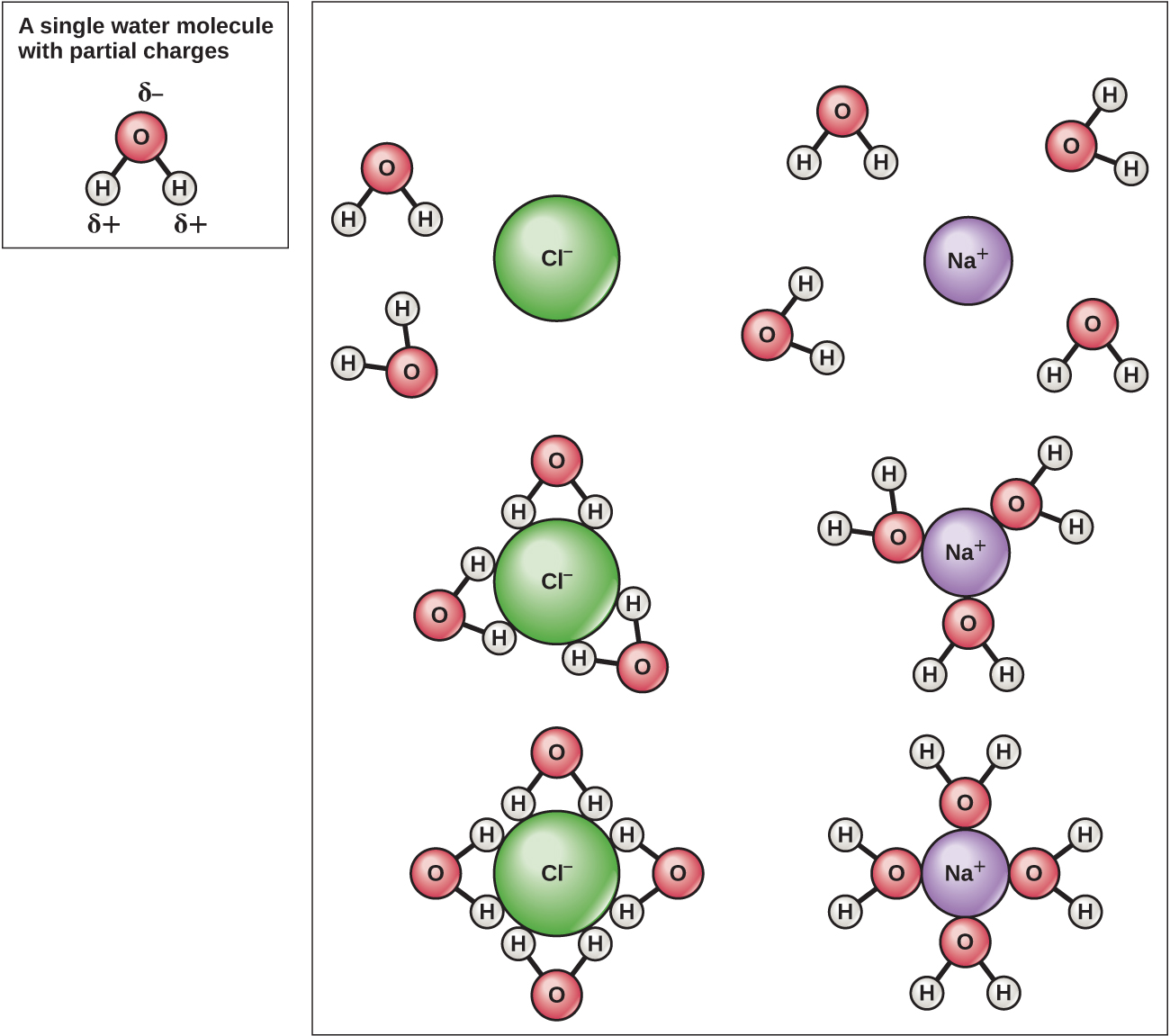
Because water is polar, with slight positive and negative charges, ionic compounds and polar molecules can readily dissolve in it. Water is, therefore, what is referred to as a solvent—a substance capable of dissolving another substance. The charged particles will form hydrogen bonds with a surrounding layer of water molecules. This is referred to as a sphere of hydration and serves to keep the ions separated or dispersed in the water ( [link] ). These spheres of hydration are also referred to as hydration shells. The polarity of the water molecule makes it an effective solvent and is important in its many roles in living systems.
The ability of insects to float on and skate across pond water results from the property of cohesion . In cohesion, water molecules are attracted to each other (because of hydrogen bonding), keeping the molecules together at the liquid-air (gas) interface. Cohesion gives rise to surface tension, the capacity of a substance to withstand rupture when placed under tension or stress.
These cohesive forces are also related to water’s property of adhesion , or the attraction between water molecules and other molecules. This is observed when water “climbs” up a straw placed in a glass of water. You will notice that the water appears to be higher on the sides of the straw than in the middle. This is because the water molecules are attracted to the straw and therefore adhere to it.
Cohesion and adhesion are also factors in bacterial colonies and biofilm formation. Cohesion keeps the colony intact (helps it “stick” to a surface), while adhesion keeps the cells adhered to each other. Cohesive and adhesive forces are important for sustaining life. For example, because of these forces, water in natural surroundings provides the conditions necessary to allow bacterial and archaeal cells to adhere and accumulate on surfaces.
The pH of a solution is a measure of hydrogen ion (H + ) and hydroxide ion (OH – ) concentrations and is described as acidity or alkalinity, respectively. Acidity and alkalinity (also referred to as basicity) can be measured and calculated. pH can be simply represented by the mathematic equation, On the left side of the equation, the "p" means "the negative logarithm of " and the H represents the [H + ]. On the right side of the equation, [H + ] is the concentration of H + in moles/L . What is not represented in this simple equation is the contribution of the OH – , which also participates in acidity or alkalinity. Calculation of pH results in a number range of 0 to 14 called the pH scale ( [link] ). A pH value between 0 and 6.9 indicates an acid. It is also referred to as a low pH, due to a high [H + ] and low [OH – ] concentration. A pH value between 7.1 and 14 indicates an alkali or base. It is also referred to as a high pH, due to a low [H + ] and high [OH – ] concentration. A pH of 7 is described as a neutral pH and occurs when [H + ] equals [OH – ].

A change of one unit on the pH scale represents a change in the [H + ] by a factor of 10, a change in two units represents a change in the [H + ] by a factor of 100. Thus, small changes in pH represent large changes in [H + ].

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?